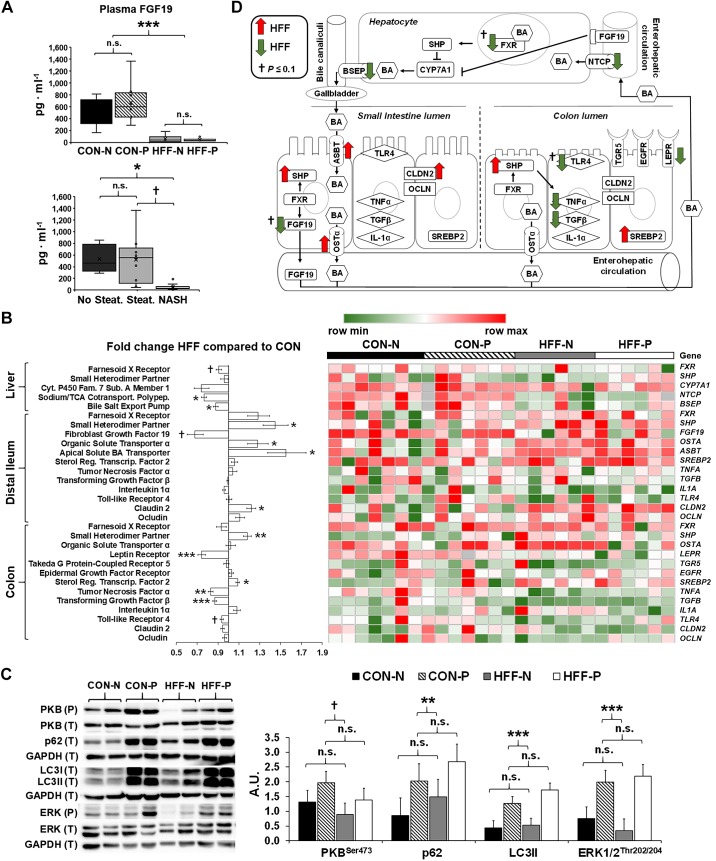
Fig. 5.
High-fructose, high-fat (HFF) diet and probiotics dysregulated enterohepatic Farnesoid-X receptor (FXR)-fibroblast growth factor 19 (FGF19) signaling and markers of autophagy in the liver. A: plasma levels of FGF19, measured by ELISA on day 70 at 8-h postfeeding, decreased in HFF compared with control (CON)-fed pigs, and in nonalcoholic steatohepatitis (NASH) compared with pigs without steatosis. N, nonprobiotic; P, probiotic. B: heat map of relative mRNA abundance of genes related to the integrity, inflammation, and proliferation of the intestinal mucosa, and enterohepatic FXR-FGF19 signaling, measured by qPCR in 83-day-old pigs, with fold change and significance levels by HFF compared with CON. Columns are individual pigs and rows are ΔCts. Green and red represent the row minimum and maximum values. Fold change calculated as 2−ΔΔCt. P values for each gene were calculated by a two-way ANOVA with a mixed model. C: representative Western blots (left) and histograms with the quantification of bands expressed as arbitrary units (A.U.; right), to assess the expression of macroautophagy-related proteins in liver tissue. Microtubule-associated protein 1A/1B light chain 3A (LC3II), ubiquitin-binding protein p62 (P62), and phosphorylated extracellular signal-regulated kinase 1/2 (ERK1/2) were significantly increased in probiotic-fed pigs, whereas phosphorylated protein kinase B (PKB) showed an increasing trend between nonprobiotic and probiotic groups. D: mechanistic illustration of genes involved in bile acid (BA)-related pathways in liver, distal ileum (DI), and colon tissue, altered by the diet. Green and red arrows represent increased and decreased expression in HFF-fed pigs compared with CON, respectively. Values in A and C are least square means ± SE. P values in A and C were adjusted for multiple testing with Tukey’s post hoc test. †P ≤ 0.1, *P ≤ 0.05, **P ≤ 0.01, ***P ≤ 0.001. n.s., Nonsignificant. ASBT, apical sodium-dependent bile acid transporter; BSEP, bile salt export pump; CLDN2, claudin-2; CYP7A1, cholesterol 7α-hydroxylase; EGFR, epidermal growth factor receptor; LEPR, leptin receptor; NTCP, Na+-taurocholate cotransporter; OCLN, occludin; OSTα, organic solute and steroid transport; SHP, small heterodimer partner; SREBP2, sterol response element-binding protein 2; TGF-β, transforming growth factor-β; TGR5, Takeda G protein-coupled receptor 5; TLR4, Toll-like receptor 4.