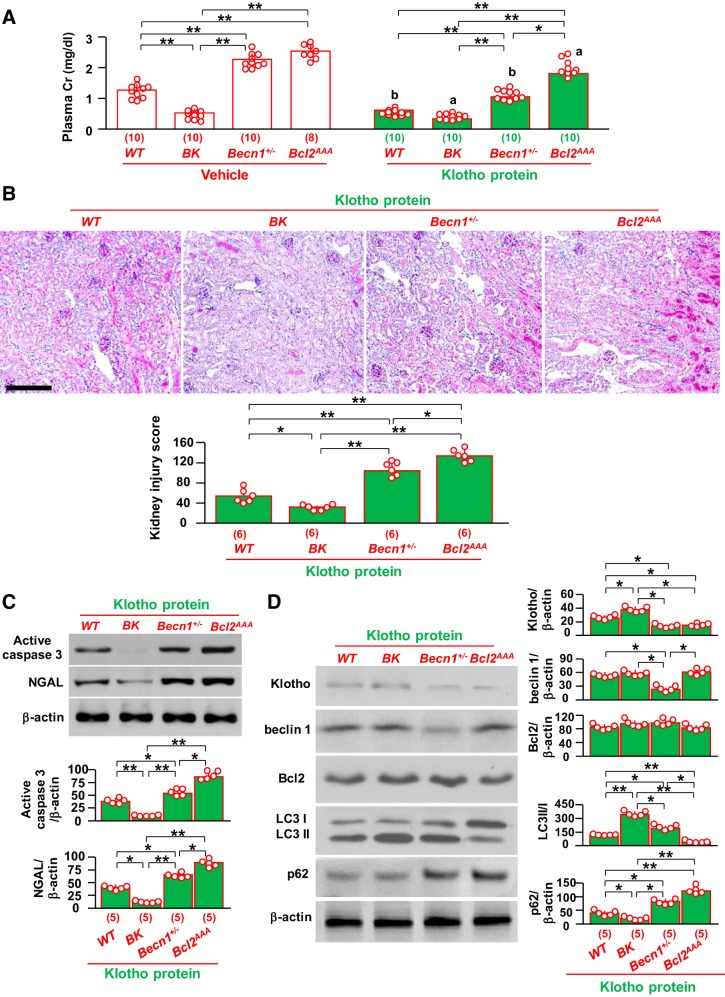
Fig. 6.
Exogenous Klotho protein is less effective in attenuating ischemia-reperfusion injury in mice with low beclin 1 activity. BK, Becn1+/−, and Bcl2AAA mice and wild-type (WT) littermates were subjected to ischemia-reperfusion followed by an immediate one-time intraperitoneal injection of recombinant Klotho protein (0.1 mg/kg body wt). Two days after surgery, mice were euthanized, blood was drawn, and kidneys were harvested. A: plasma creatinine (Cr). Data are expressed as means ± SD, and statistical significance was evaluated by two-way ANOVA followed by a Student-Newman-Keuls post hoc test; significance was accepted when *P < 0.05 and **P < 0.01 between two groups. aP < 0.05 and bP < 0.01 between vehicle- and Klotho-injected groups of the same genotype of mice. B: kidney histology of Klotho-injected acute kidney injury (AKI) mice. Top, representative microscopic images of periodic acid-Schiff (PAS) staining. Scale bar = 200 μm. Bottom, semiquantitative assessment of kidney injury score based on PAS stain in each group. C: kidney damage markers in Klotho-injected mice. Top, representative immunoblots for active caspase-3 and neutrophil gelatinase-associated lipocalin (NGAL) proteins in total kidney lysates. Bottom, summary of all immunoblots from each group. D: changes in autophagic markers in kidneys of Klotho-injected AKI mice. Left, representative immunoblots for Klotho, beclin 1, Bcl-2, light chain (LC)3, and p62 in total kidney lysates. Right, summary of all immunoblots from each group. Data are expressed as means ± SD, and statistical significance was evaluated by one-way ANOVA followed by a Student-Newman-Keuls post hoc test; significance was accepted when *P < 0.05 and **P < 0.01 between two groups for B–D. Sample numbers in each group are presented in brackets underneath the corresponding bars.