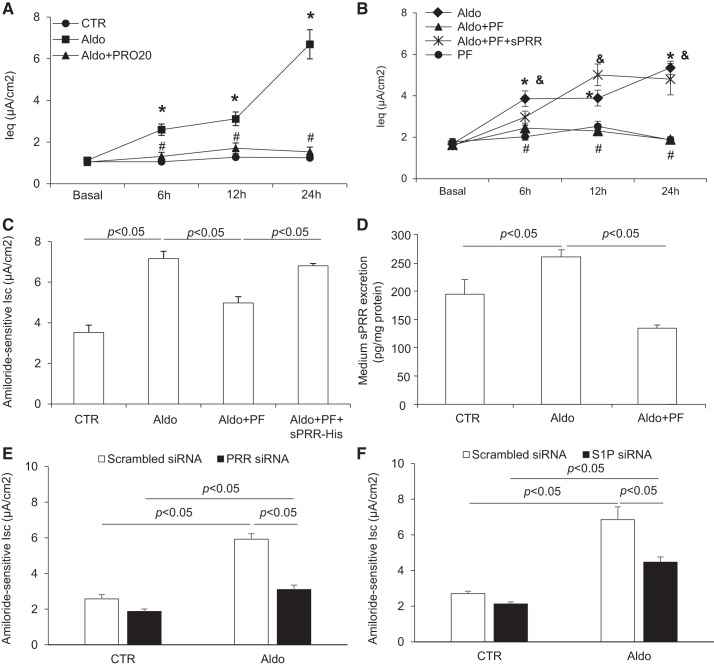
Fig. 5.
Site-1 protease (S1P)-derived soluble (pro)renin receptor (sPRR) mediated aldosterone (Aldo)-induced epithelial Na+ channel (ENaC) activation. Confluent mpkCCD cells grown on Transwells or Snapwells were pretreated with 10 μM PF-429242 (PF) or 1.5 μM PRO20 for 1 h and then treated with 1 μM Aldo and 10 nM histidine-tagged sPRR (sPRR-His). Transepithelial Na+ transport was recorded using an epithelial volt ohmmeter (A and B) and the Ussing chamber technique (C). Medium sPRR was measured using ELISA. A: time course of equilibrium current (Ieq) changes in control (CTR), Aldo, and Aldo + PRO20 groups over 24 h. *P < 0.05 vs. CTR; #P < 0.05 vs. Aldo. B: time courses of Ieq changes in Aldo, Aldo + PF, Aldo + PF + sPRR-His, and PF groups. *P < 0.05 vs. the Aldo group; #P < 0.05 vs. the Aldo + PF + sPRR-His group; &P < 0.05 vs. PF. C: amiloride-sensitive current in CTR, Aldo, Aldo + PF, and Aldo + PF + sPRR-His groups at 12 h. D: medium sPRR content in CTR, Aldo, and Aldo + PF groups. E: effect of Aldo on ENaC activity in the presence or absence of PRR siRNA. F: effect of Aldo on ENaC activity in the presence or absence of S1P siRNA. Data are means ± SE; n = 4–5 per group for A–F.