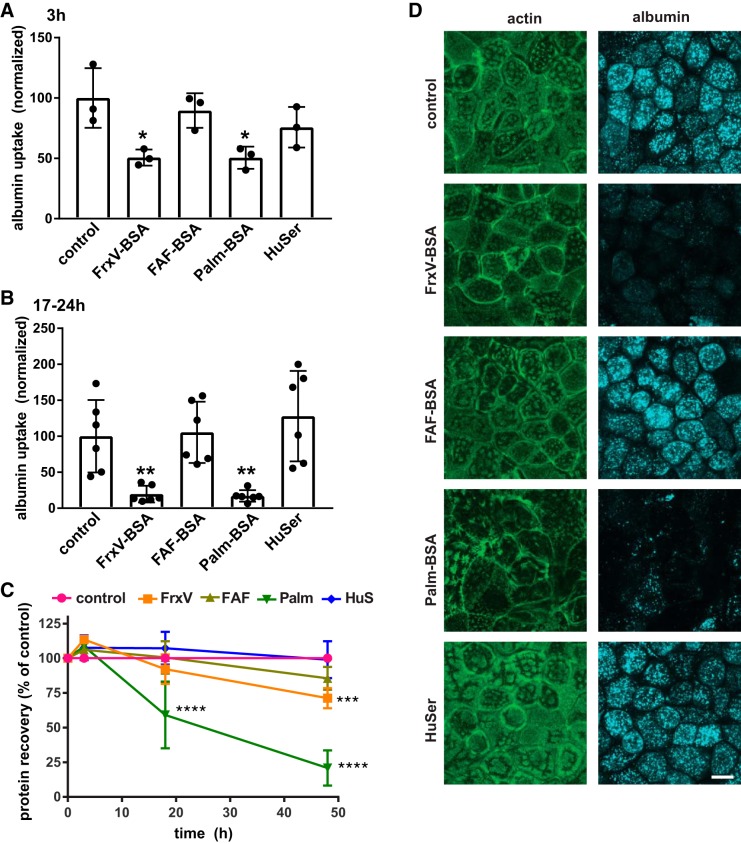
Fig. 1.
Differential effect of albumin ligands with proximal tubule (PT) endocytic capacity. Opossum kidney (OK) cells were incubated for 3 h (A) or 17–24 h (B) in serum-free medium without (control) or with apically added BSA [20 mg/mL fraction V BSA (FrV-BSA), fatty acid-free BSA (FAF-BSA), or palmitate-loaded BSA (Palm-BSA)] or 50% human serum (HuSer), as noted. Cells were then rinsed several times and incubated for 30 min with Alexa Fluor-647 albumin, and cell-associated fluorescence was quantified by spectrofluorimetry. Data were normalized to the protein recovered in each sample. The mean control uptake of all experiments was set to 100, and each point represents data from an independent experiment. *P < 0.02 and **P ≤ 0.01 by one-way ANOVA (Dunnett’s multiple-comparisons test). C: recovered protein concentrations (means ± SD, normalized to control) from cells treated for 3–48 h with albumin or HuSer as above. ***P ≤ 0.0005 and ****P ≤ 0.0001 by one-way ANOVA (Dunnett’s multiple-comparisons test): 3 h, n = 3; 17–24 h (combined), n = 9; 48 h, n = 5. D: control cells or cells treated overnight with albumin or HuSer and incubated for 30 min with Alexa Fluor-647 albumin (blue) were fixed and processed to detect actin (green). Maximum projections sections of confocal stacks are shown to confirm that exposure to FrxV-BSA or Palm-BSA reduces cellular albumin uptake and alters cell morphology but does not affect the integrity of the monolayer. Scale bar = 10 µm.