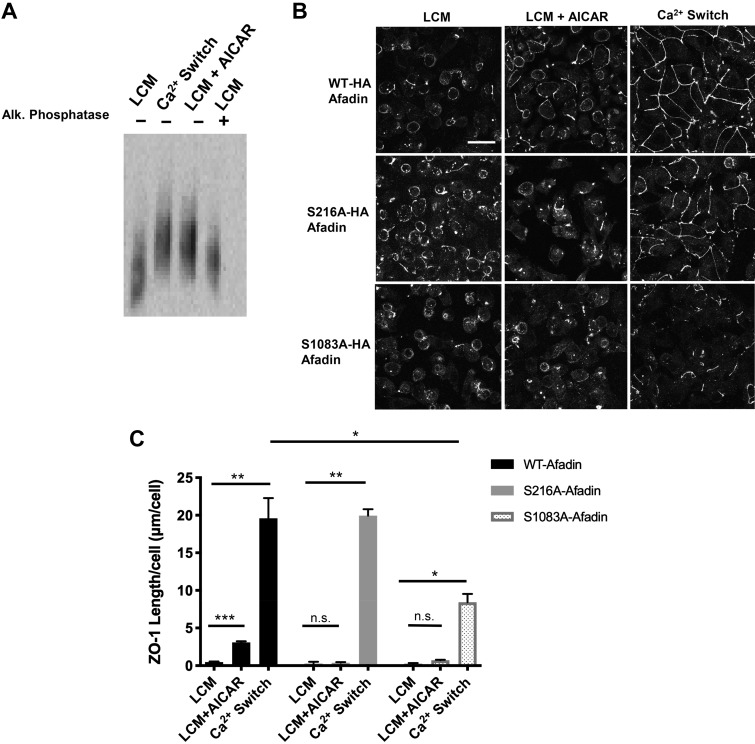
Fig. 6.
Afadin phosphorylation is an important component of AICAR- and Ca2+ switch-mediated junction assembly. A: confluent Madin-Darby canine kidney (MDCK) cells were incubated in media containing 5 μM Ca2+ [low-Ca2+ media (LCM)] for 16 h. Fresh LCM with or without 2 mM AICAR or media containing 1.8 mM Ca2+ (Ca2+ switch) were introduced for 2 h. Alkaline phosphatase treatment was performed at 37°C for 1 h. Cell lysates were separated by phos-tag acrylamide gel electrophoresis. Western blot analysis was used to probe for protein expression with the anti-Afadin antibody. B: confluent MDCK cells stably transfected with hemagglutinin (HA)-tagged afadin corresponding with the wild-type mus musculus cDNA sequence (top) or containing the S216A or S1083A mutations (bottom) were incubated in media containing 5 μM Ca2+ (LCM) for 16 h. Fresh LCM with or without 2 mM AICAR or media containing Ca2+ switch were introduced for 2 h. Cells were fixed and immunostained for zonula occludens-1 (ZO-1). Scale bar, 30 μm. C: quantification of ZO-1 localization at sites of junction assembly. Data were analyzed for each experimental condition based on four randomly obtained views from three independent coverslips. Error bars represent the SE of the length of ZO-1 per cell within each of the four selected fields of view. *, **, or ***Significant difference in ZO-1 length due to the Ca2+ switch (P < 0.01) or AICAR (P < 0.001) in cells with WT-afadin and in cells with S216A afadin (P < 0.01) or S1083A afadin (P < 0.05) due to the Ca2+ switch relative to their respective LCM conditions. There was also a significant difference in ZO-1 length in response to the Ca2+ switch in cells with S1083A afadin versus WT cells. P values were calculated based on the two-way ANOVA with Sidek’s multiple-comparisons test.