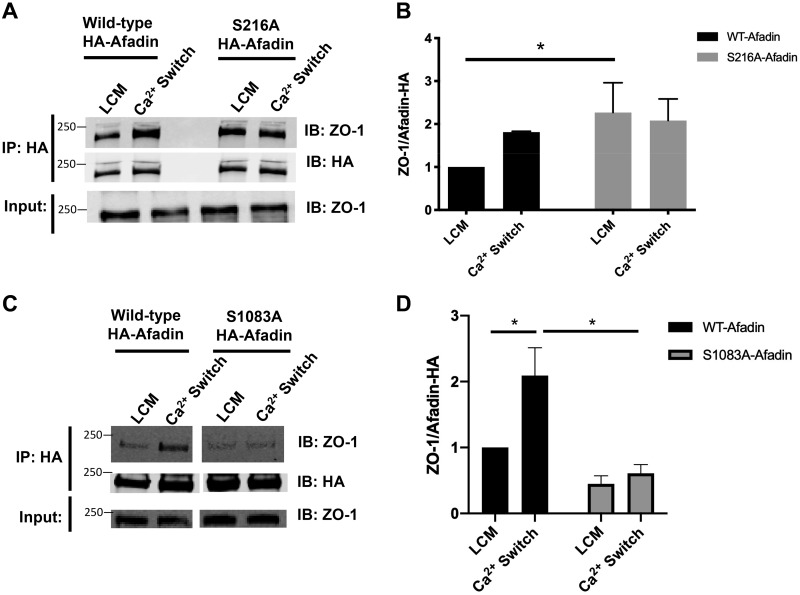
Fig. 7.
S216A and S1083A mutations in afadin influence its interaction with zonula occludens-1 (ZO-1). A and C: confluent Madin-Darby canine kidney (MDCK) cells stably transfected with hemagglutinin (HA)-tagged afadin corresponding with the wild-type (WT) mus musculus cDNA sequence; the S216A or the S1083A mutation was incubated in media containing 5 μM Ca2+ [low-Ca2+ media (LCM)] for 16 h. Fresh LCM or media containing 1.8 mM Ca2+ (Ca2+ switch) for 2 h. Cell lysates from each condition were obtained and immunoprecipitated with HA-antibody conjugated beads. Equal amounts of immunoprecipitates (IP) were then separated on SDS-PAGE and probed with anti-ZO-1 and anti-HA antibody. Total cells lysates were simultaneously subjected to immuoblotting (IB) using anti-ZO-1 antibody. B and D: quantification of the immunoreactive signal for ZO-1 in immunoprecipitates normalized to the level of immunoprecipitated HA-tagged afadin. Data were analyzed for each experimental condition based on three independent experiments and represent mean intensity relative to LCM (WT) level ± SE. *Significant difference in the amount of ZO-1 coimmunopreciptated with HA-afadin in cells with S216A HA-afadin compared with WT HA-afadin under LCM conditions (P < 0.05) and in cells with S1083A HA-afadin compared with WT HA-afadin under Ca2+ switch conditions (P < 0.05) based on the two-way ANOVA with Sidek’s multiple-comparisons test.