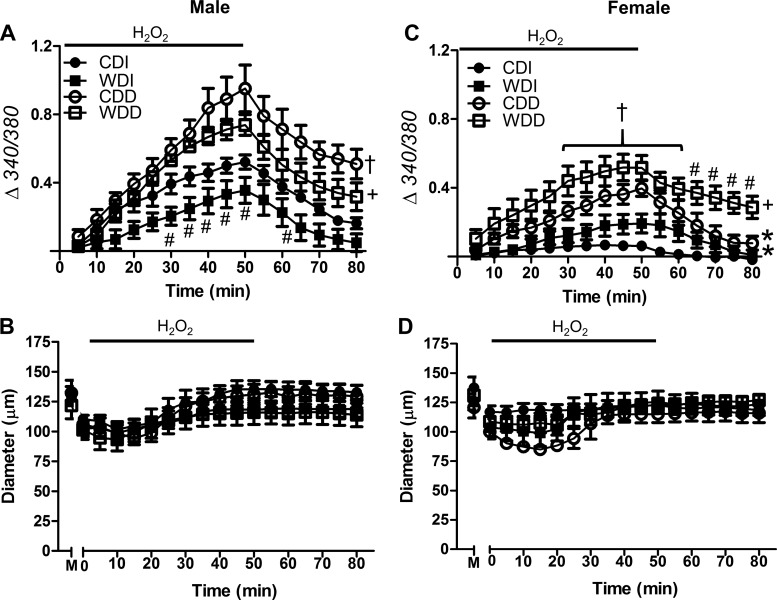
Fig. 3.
Effect of H2O2 exposure on cytosolic Ca2+ concentration ([Ca2+]i) in the vessel wall. A and C: [Ca2+]i responses with fura 2 (Δ340/380) during 50-min exposure to H2O2 (200 μM) followed by 30-min washout in standard PSS. Data are for intact and endothelium-disrupted SEAs from male (A) and female (C) mice fed the control diet (CD) or Western-style diet (WD). Compared with the CD, the WD reduced the [Ca2+]i response to H2O2 primarily in males; endothelial disruption increased [Ca2+]i responses in all groups and impaired recovery for each group except females fed the CD. B and D: internal diameters were not different between intact and endothelium-disrupted SEAs from males (B) or females (D). M, maximal diameter in Ca2+-free PSS. Values are means ± SE; n = 4–8 vessels per group. #P < 0.05, WD vs. respective CD. †P < 0.05, endothelium-disrupted vs. -intact within CD. +P < 0.05, endothelium-disrupted vs. -intact within WD. *P < 0.05, female vs. male for CDI and CDD. CDI, CD intact endothelium; WDI, WD intact endothelium; CDD, CD disrupted endothelium; WDD, WD disrupted endothelium.