Fig. 7.3.
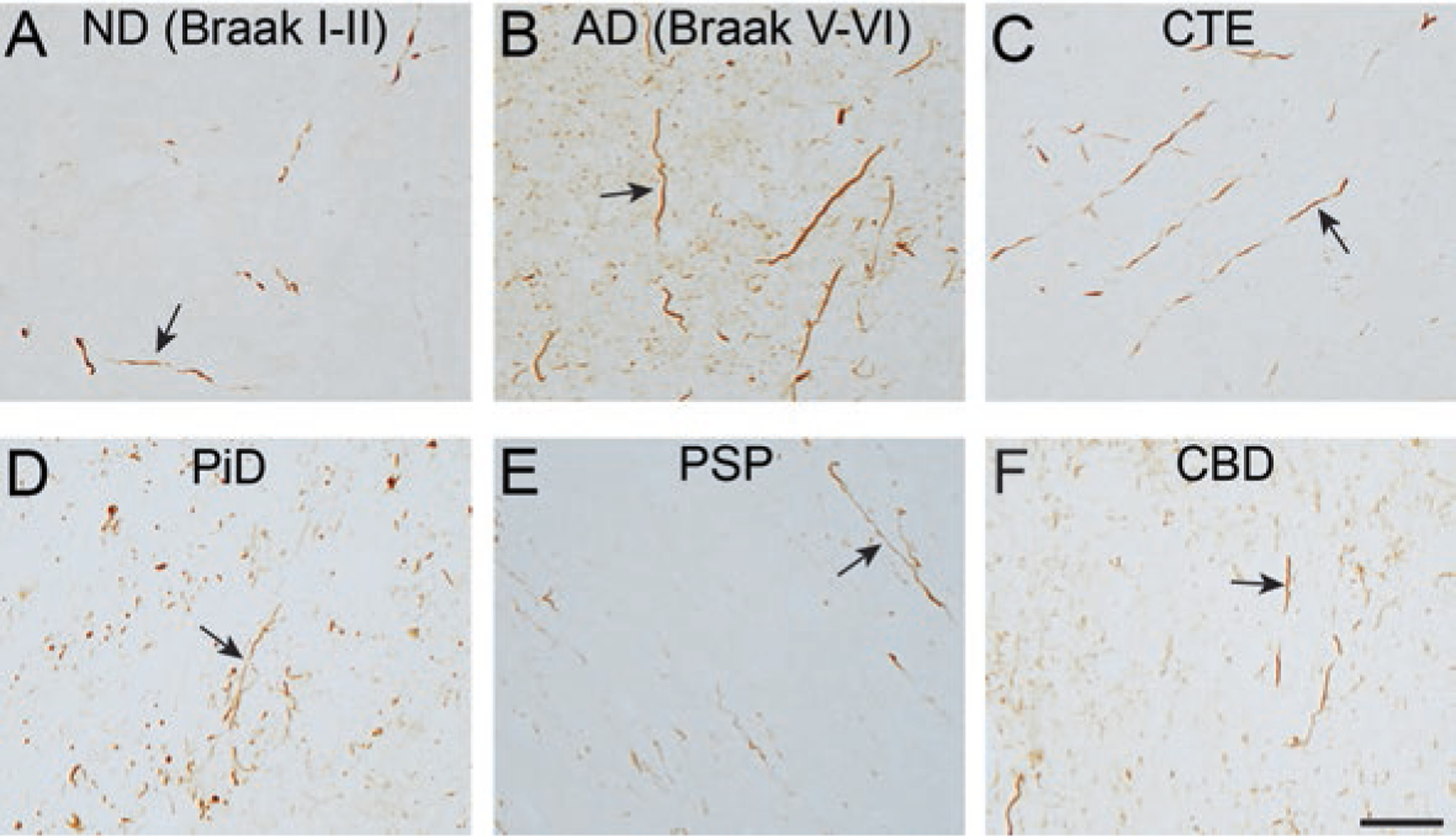
Dystrophic axons containing tau pathology is a prominent feature in multiple tauopathies. The TNT1 antibody detects exposure of the phosphatase activating domain (PAD). (a, b) TNT1 pathology-containing axons are observed in the subcortical white matter in non-demented aged patients with early stages of tau deposition (a; ND (Braak stage I-II)) and robust TNT1 axonal pathology is seen in severe Alzheimer’s disease brains (b; AD (Braak stage V-VI). C-F) Axonal tau pathology in the subcortical white matter displays PAD exposure (i.e. TNT1 reactivity) in chronic traumatic encephalopathy (c; CTE), Pick’s disease (d; PiD), progressive supranuclear palsy (e; PSP) and corticobasal degeneration (f; CBD) as well. Scale bar is 50 μm
