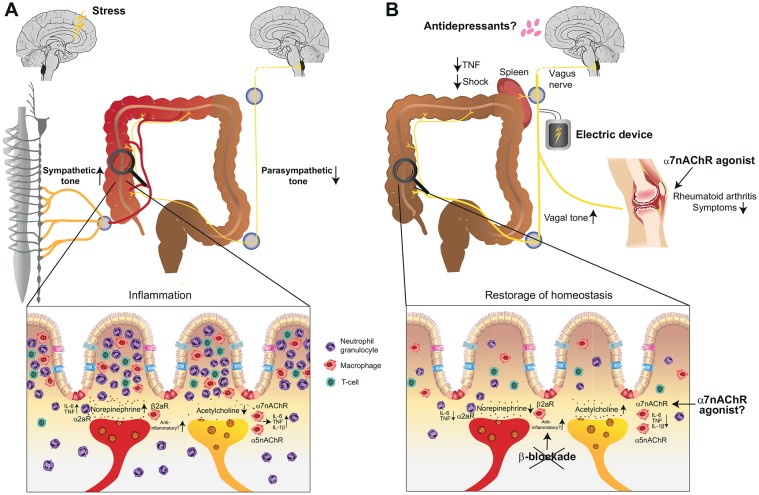
Figure 4.
Involvement of the autonomous nervous system in the pathogenesis of inflammatory bowel disease (IBD) and available treatment modalities that harness neuro-immune interactions. (A) Stress and the transmitted signals may enhance the sympathetic tone and lead to an additional pro-inflammatory reaction in the intestine that may be causal or at least worsening the course of IBD. Failure to maintain an adequate parasympathetic tone can further support the pro-inflammatory reaction. (B) Available treatment options in chronic inflammatory conditions include electric stimulation of the vagal nerve in rheumatoid arthritis, IBD and endotoxin-induced septic shock. Furthermore, the repertoire of treatment strategies for IBD and rheumatoid arthritis may be extended with α7nAChR-agonists. β-blockade should, however, be omitted in IBD. α7nAChR, alpha7 nicotinic acetylcholine receptor; α5nAChR, alpha5 nicotinic acetylcholine receptor; α2aR, alpha2 receptor; β2aR, beta-2 adrenergic receptor; TNF, tumor necrosis factor alpha.