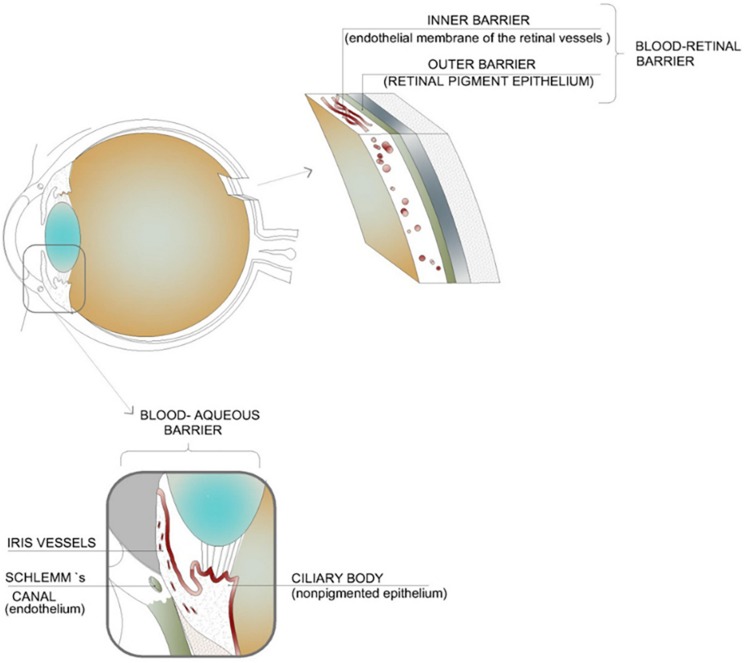
FIGURE 2.
Illustration of the blood–ocular barriers which inhibit the movement of active ingredients into the eye from systemic circulation; namely, the blood–aqueous barrier and the blood–retinal barrier. These barriers result in the need for high systemic dosages of drugs in order to achieve an adequate concentration within the intended tissues. This high dosage can lead to unwanted side effects (adapted with permission from Occhiutto et al., 2012).