Figure 2. Neuroprotective properties of GT949 in bilaminar cultures after acute exposure to glutamate (in the absence of glia).
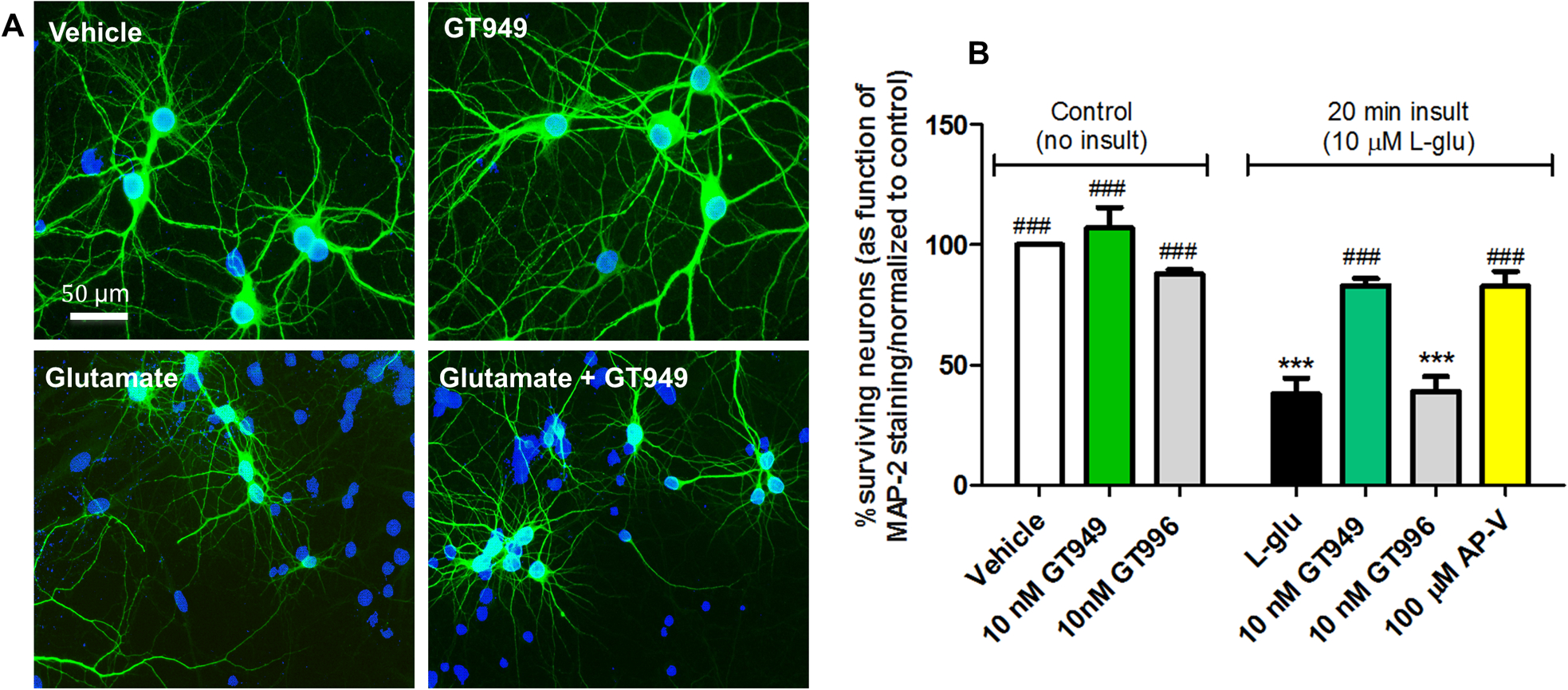
A. Representative images of cultures after different treatments in the absence of glia. The neuronal layer of bilaminar cultures was immunostained against MAP-2 (green), and counterstained with the nuclear marker DAPI (blue). Cultures exposed to vehicle, or 100 nM GT949 alone do not display obvious degeneration or cell death. Cultures acutely exposed to L-glutamate (20 min, 10 μM) show increased DAPI positive, MAP-2 negative cells, indicative of toxicity and neuronal death. However, co-exposure of 10 nM GT949 reversed a portion of the cellular damage caused by L-glutamate. All images are shown at 40x magnification. Scale bar: 50 μm.
B. Quantification of neuronal survival in the absence of glia. After vehicle or L-glutamate (20 min, 10μM) exposure in glia-free conditions, coverslips were transferred back to their original glia dishes in the presence or absence of GT949 or GT996 (10nM) or the NMDA antagonist AP-V (100μM) for 24 hours. Then, cells were fixed and immunostained as in A, and analyzed for cell death. GT949 and GT996 alone did not alter neuronal survival levels. Acute L-glutamate significantly decreased neuronal survival, while GT949, and AP-V mitigated L-glutamate neurotoxicity. GT996, the inactive analog, had no effect on neuronal survival after L-glutamate exposure. Data was normalized to control, 3–4 coverslips were assessed per treatment condition and 100–150 cells were manually counted per treatment. Neuronal survival data is representative of 3 independent experiments, and control levels were not statistically different for normalization purposes. ***p<0.001, vs. vehicle (no insult), ###p<0.001, vs. insult.
