Figure 3. Lack of neuroprotective properties of GT949 in bilaminar cultures after acute exposure to H2O2-mediated oxidative stress.
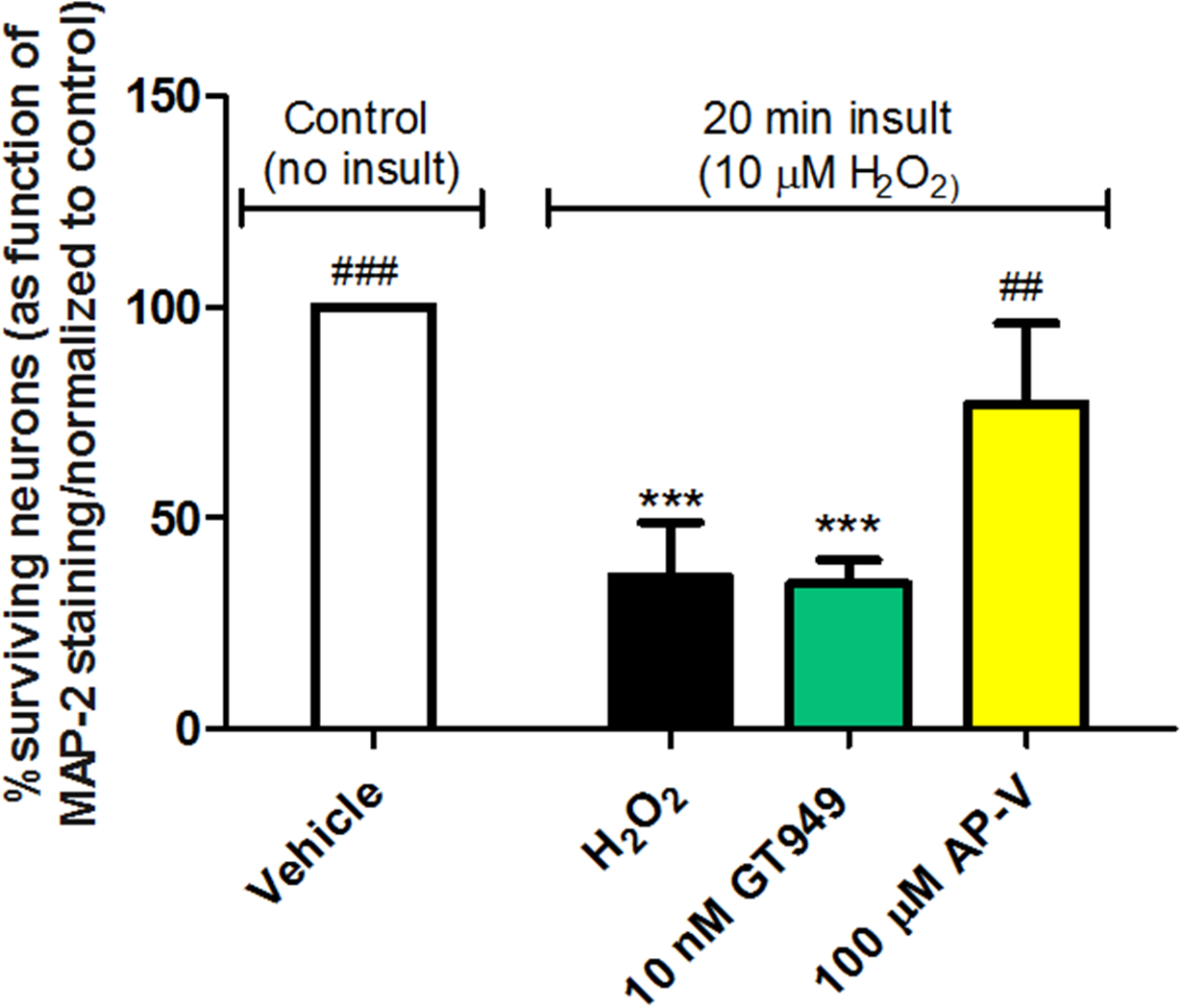
Bilaminar cultures at 14 DIV were treated with conditioned medium containing 10 μM H2O2 for 20 minutes, followed by replacement of the H2O2 medium and compound treatment for 24 hours. Neurons were then fixed and immunostained against MAP-2 for downstream survival analysis. Exposure significantly reduced neuronal survival, and co-treatment with 10 nM GT949 was not neuroprotective. Co-treatment with 10 nM GT996 also had no effect on neuronal survival after H2O2 exposure. However, Co-treatment with 100 μM AP-V did significantly reverse H2O2-induced neuronal death, suggesting that NMDA receptor activation is involved in oxidative stress-mediated neuronal toxicity. Survival quantification was normalized to control cultures. 3–4 coverslips were assessed per treatment condition and 100–150 cells were manually counted per treatment. Neuronal survival data is representative of 3 independent experiments and control levels were not statistically different for normalization purposes. ****p<0.0001, vs. control (no insult), ###p<0.001, ##p<0.01, vs. insult.
