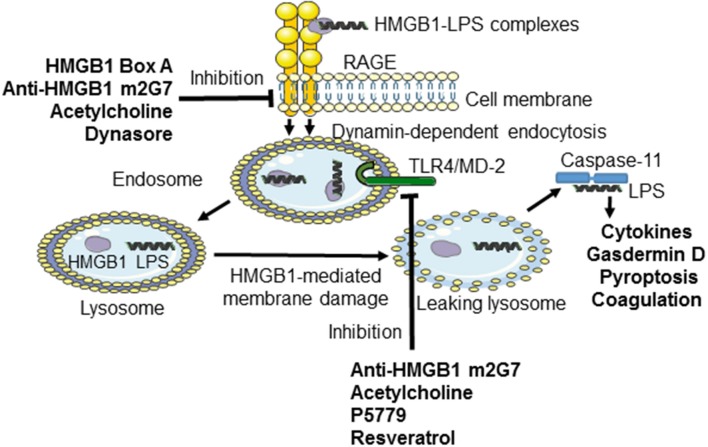
Figure 1.
Inhibiting TLR4- or RAGE-mediated effects induced by HMGB1 or LPS-HMGB1 complexes. During endotoxemia, LPS and extracellular HMGB1 forms complexes that are endocytosed via the RAGE-dependent pathway. LPS and HMGB1 activate TLR4 system. The unique contribution by HMGB1 is disruption of the lysosomal membrane enabling LPS to reach and activate its cytosolic receptor caspase-11, which cleaves gasdermin D to form an active oligomer. Activated gasdermin D will subsequently start coagulation and cause cellular pyroptosis in murine macrophages. The HMGB1-specific inhibitors recombinant HMGB1 box A, anti-HMGB1 m2G7, and acetylcholine each inhibits the cellular internalization of LPS-HMGB1 complexes and resultant immune activation. Anti-HMGB1 m2G7 and acetylcholine also inhibit HMGB1/TLR4-mediated inflammation, whereas P5779 and resveratrol selectively block the HMGB1/TLR4 pathway only.