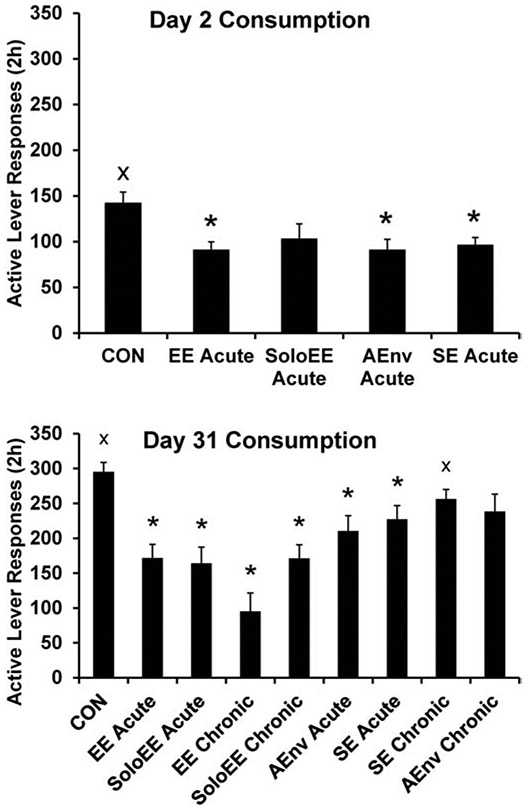
Fig. 4.
Parametric evaluation of components of EE that contribute to the anti-taking effect of EE. Sucrose taking (consumption) was assessed for 2 h either two or 31 days following sucrose self-administration training. Some subjects received EE or components of EE for the 22 h prior to seeking testing (Acute) on Day one or 30 of abstinence or over 29 days of abstinence (Chronic) prior to seeking testing on Day 30. Components were experiencing the EE cage alone (SoloEE), being paired in a double-sized cage with a conspecific (SE), or being housed singly in a novel cage of similar size to Control housing (AEnv). * indicates significant difference from Control; x indicates significant difference from EE Acute, P < .05. Means ± SEMs indicated on figures. Figures reproduced from “Brief exposure to novel or enriched environments reduces sucrose cue-reactivity and consumption in rats after 1 or 30 days of forced abstinence from self-administration,” by J.W. Grimm, R. Weber, J. Barnes, J. Koerber, K. Dorsey, and E. Glueck, 2013, PLoS One, 8:e54164. Copyright 2013 by the authors.