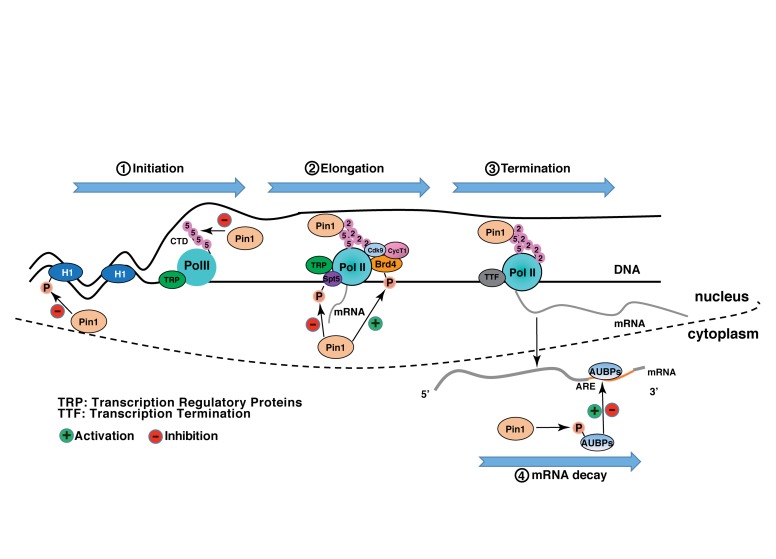
FIGURE 2.
Pin1 regulates gene expression network. During transcription initiation, Pin1 promotes dephosphorylation of Histone H1 and Ser5 in the CTD of RNA polymerase II, to inhibit the recruitment of TRP (transcription regulatory proteins) and pre-initiation complex, and promoter clearance, processes that are required to transcription initiation. During transcription elongation, on one hand, Pin1 binds to phosphorylated Spt5 and might facilitate conversion of DSIF from a negative elongation factor into a positive elongation factor. On the other hand, Pin1 enhances Brd4’s stability and its interacting with CDK9 to phosphorylate Ser2 in the CTD of RNA polymerase II, and thus increases transcription elongation. In transcription termination, Pin1 binds to phosphorylated Ser2 in the CTD of RNAPII and facilitates coordinate recruitment of TTF (transcription termination factors). After the synthesis of mRNA, Pin1 binds to AUBPs (AU-binding proteins) to accelerate or slow mRNA decay.