Fig. 20.
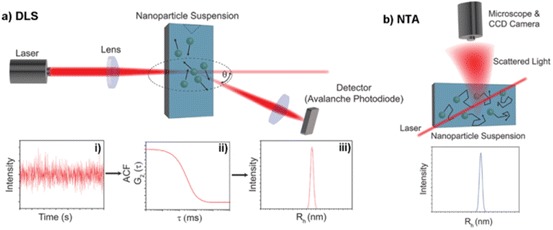
Dynamic light scattering (DLS) and nanoparticle tracking analysis (NTA) as tools for determining NP hydrodynamic radius (R h). a (i) DLS estimates R h through ensemble measurements of scattering intensity at angle θ over time; (ii) autocorrelation functions (ACF) are generated from which a diffusion constant (D) is estimated; (iii) R h is calculated from the estimated D via the Stokes–Einstein equation, and analysis of many ACF is combined to generate a histogram of R h vs. intensity. b NTA tracks the movement of individual NPs; R h is calculated for each particle, giving NTA greater resolution and no intensity bias to larger NPs
