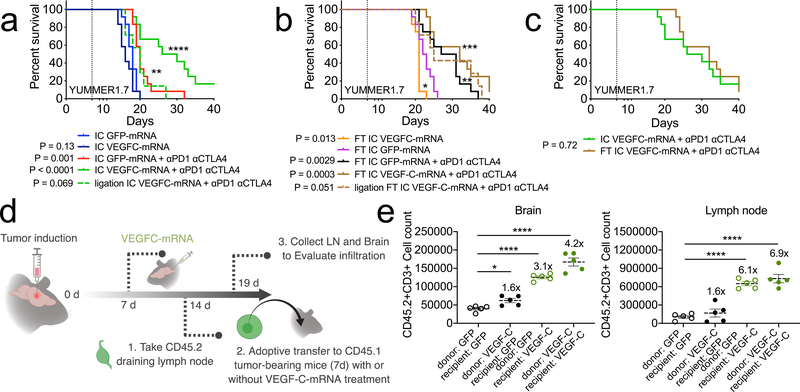
Figure 4. T cell extrinsic VEGF-C signaling mediates protection against intracranial tumor and is equivalent to peripheral priming.
a-c mice were given either only YUMMER1.7 intracranial tumors (IC, a) or a YUMMER1.7 flank tumor and YUMMER1.7 intracranial tumor (FT, b) and treated with GFP/VEGF-C-mRNA on day 7 and anti-PD1 (RMP1–14), anti-CTLA4 (9H10) on days 7, 9 and 11. (a, n = 12 for all groups except ligation IC VEGFC-mRNA + αPD1 αCTLA4, n = 7; b, n = 12 for all groups except ligation FT IC VEGFC-mRNA + αPD1 αCTLA4, n = 7). d Schematic for experiment design of e. Congenic CD45.2 mice were injected with GL261 tumors. 7 days post tumor inoculation (pti), mice were treated with GFP-mRNA or VEGF-C-mRNA. At 7 days post mRNA-treatment (14 day-pti) leukocytes from dcLNs were transferred into congenic CD45.1 mice bearing 7 day-tumors. Five days after transfer, dcLNs and brain tissues were harvested to analyze T cell infiltration. e Quantification of brain infiltrating and lymph node T cells (n = 5 animals, all groups). Data are mean ± S.E.M *P < 0.05; **P < 0.01; ***P <0.001; ****P<0.0001 (two-tailed unpaired Student’s t-test, two-sided Log-rank Mantel-Cox test)