Fig. 3.
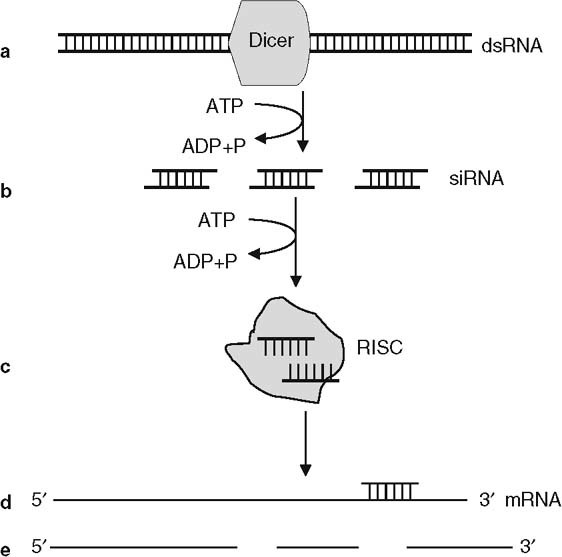
Hypothetical model of RNA interference. (a) When introduced into a cell, double-stranded (ds)RNA is cleaved into small interfering (si)RNAs by a Dicer nuclease in an adenosine triphosphate (ATP)-dependent process. (b) Duplex siRNAs are recruited by several intracellular proteins, forming the RNA-induced silencing complex (RISC). (c) Unwinding of duplex siRNA occurs in an ATP-dependent manner. (d) The antisense strand of the siRNA binds to the messenger (m)RNA. (e) Activation of nuclease activity leads to degradation of the target mRNA. ADP = adenosine diphosphate; P = phosphate.
