Figure 1.
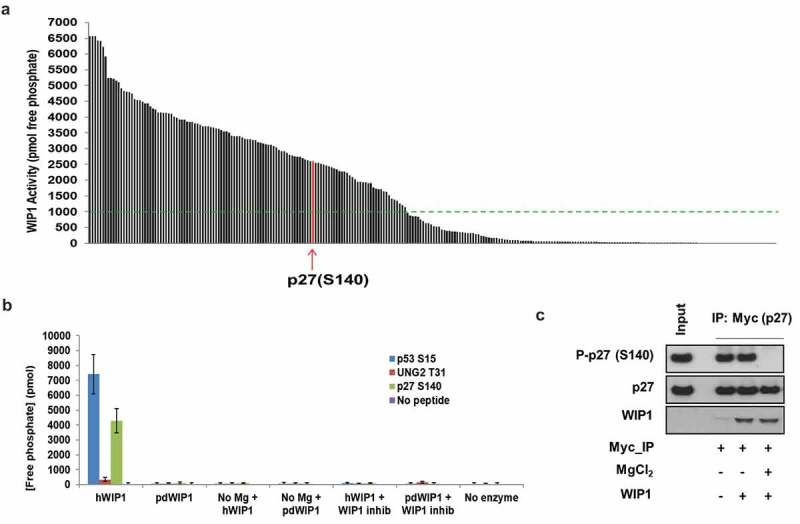
WIP1 dephosphorylates p27Kip1 in vitro. (a) WIP1 target screening by in vitro phosphatase assay. Here, 264 synthetic 11 amino acid phosphopeptides (China Peptides Co.) were incubated with purified active WIP1 enzyme in the presence of Mg2+. The release of free phosphate from each of the phosphopeptides was quantified to determine phosphatase activity. Arrow indicates the location of p27Kip1 (CDKN1B) S140 phosphopeptide in relation to all others in the screen. Samples are duplicated for the assay. The green dotted line indicates the threshold value of 1000 pmol free phosphate released in the assay. We considered all phosphopeptides above that value to be strong candidate WIP1 target sites. The list of candidate phosphopeptides and WIP1 activity in the presence of each is indicated in Table S1. (b) Further validation of WIP1 dephosphorylation of p27Kip1 at serine 140. The 11 amino acid phosphopeptide including the central S140 residue was incubated with WIP1 and WIP1 D314A (phosphatase-dead mutant). WIP1-specific inhibitor GSK2830371 was used at 3 µM concentration. WIP1 enzyme without Mg2+ is used as a control. p53 pS15 and UNG2 pT31 are the positive [14] and negative [30] controls for WIP1 activity, respectively. Samples were assayed in duplicate. (c) WIP1 dephosphorylates intact p27Kip1 in vitro after p27Kip1 purification from HEK293 cells. After overexpression of wild-type Myc-p27Kip1 in HEK293 cells, the cells were irradiated with 10 Gy IR (0.5 h recovery) and then lysed in lysis buffer. Myc-p27Kip1, precipitated with anti-Myc antibody and purified from the HEK293 cell lysates, was incubated with purified recombinant WIP1 to assess phosphatase activity. The proteins were resolved on SDS-PAGE and followed by immunoblot analysis using anti-WIP1, anti-p27Kip1 protein, and anti-p27Kip1 pS140 antibodies.
