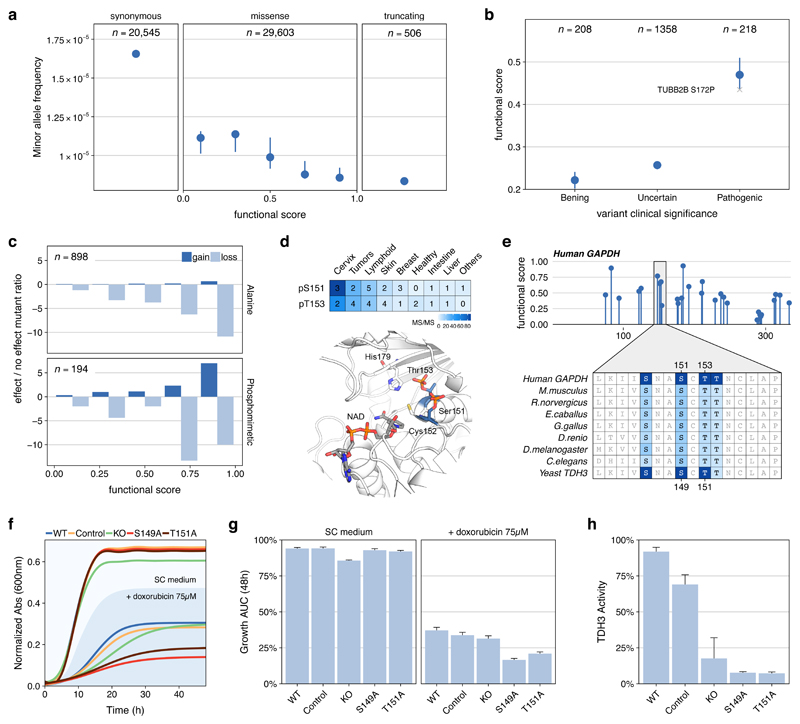
Figure 4. Consequences of genetic variants for phosphosites with high functional scores.
a) Median (CI > 95%) minor allele frequency for variants sorted by phosphosite functional score and compared with synonymous and stop codon causing variants occurring at phosphosite positions. b) Mean functional score (CI > 95%) for phosphosites at positions with mutations found in patients and having benign, uncertain or pathogenic consequences. The S172P mutation in Tubulin, Beta 2B (TUBB2B) is highlighted as an example - see main text c) Fold ratio of mutations in phosphorylated positions reported in mutagenesis studies having gain/loss of function effects versus no effect and stratified by functional score. d) MS evidence for the phosphorylation of S151 and T153 in GAPDH and their structural context flanking a catalytic cysteine e) Position and functional score for all GAPDH phosphosites and alignment of two human phosphosites (S151 and T153) to the corresponding S. cerevisiae TDH3 (S149 and T151). Color gradient corresponds to supporting evidence of phosphorylation based on ancestral reconstruction f) Consensus growth curves and (g) mean and standard error of the area under the growth curve for wild type (WT), control, GAPDH knockout (KO) and S149 and T151 phospho-deficient mutants in the presence or absence of doxorubicin (75 μM). Every clone is present 4 times in each plate and the experiment repeated 3 times for a total of 12 replicates. h) TDH3 activity as mean and SE measured twice in 3 independent extracts obtained from control and mutant strains.