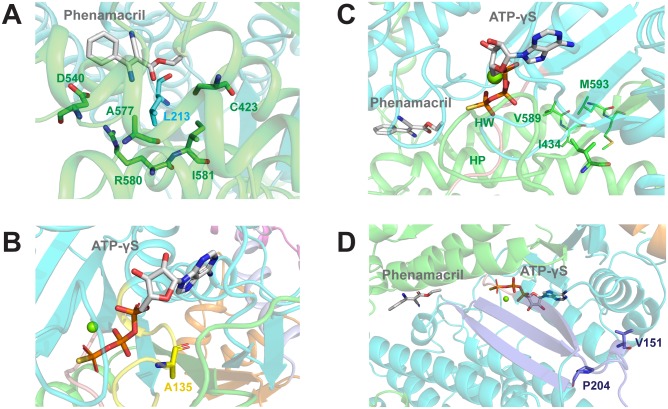
Fig 4. Localization of mutant residues that cause mild phenamacril resistance.
(A) A577, R580, and I581 are pocket residues. A577 directly interacts with phenamacril, whereas R580 and I581 interact with pocket residues L213 from U50 (cyan) and C423, D540, and A577 from L50 (green). (B) A135 is a P-loop (yellow) residue of the ATP-pocket that interacts with the α- and β-phosphates of ATP. (C) I434 of helix HP (helix 12) interacts with L588, V589, L592, and M593 of helix HW (helix 19). These interactions likely determine the orientation of the N-terminus of HP, which leads into Switch 2 and directly interacts with phenamacril. (D) V151 and P204 are residues in the Transducer (purple), which communicates conformational changes between motor and converter domains. The Transducer consists of the last three β-strands of the U50 β-sheet and Loop 1 (flanked by V151) and the P204-containing β-bulge.