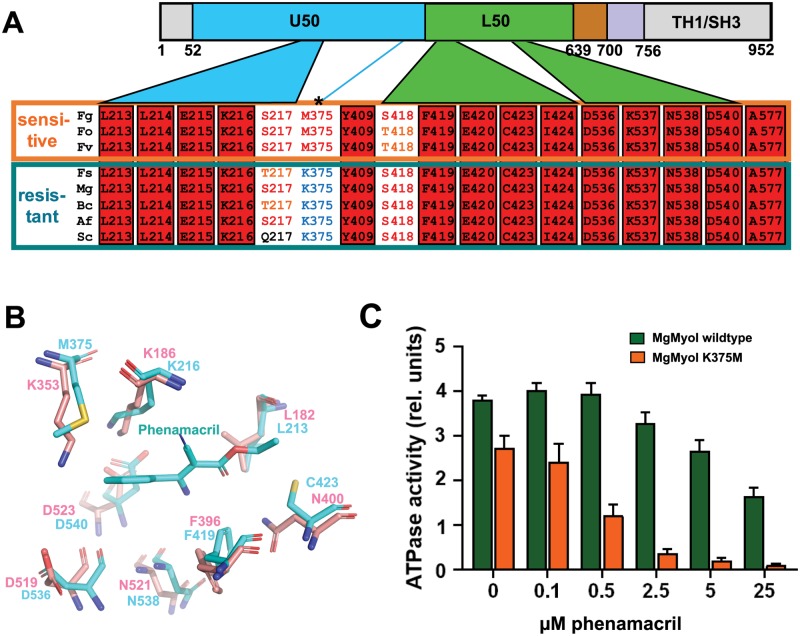
Fig 8. M375 is a major phenamacril specificity determinant.
(A) Conservation among the phenamacril pocket residues in myosin I motor domains from phenamacril-sensitive strains (Fg, Fo, Fv) and phenamacril-insensitive strains (Fs, Mg, Bc, Af, Sc). Fg: Fusarium graminearum, Fo: F. oxysporin, Fv: F. verticillioides, Fs: F. solani, Mg: Magnaporthe grisea, Bc: Botrytis cinerea, Af: Aspergillus flavus, Sc: Saccharomyces cerevisiae. (B) Overlay of FgMyoI phenamacril pocket residues (cyan) and their corresponding residues from Dictyostelium discoideum myosin I (pink, PDB 1LKX [36]). For clarity, only those residues are shown that have different side chain positions among the two myosins. (C) Mutation of MgMyoI K375 to M confers phenamacril sensitivity. ATPase activity (relative luminescence units) of purified wildtype and K375M MgMyoI/CaM in the presence of the indicated concentrations of phenamacril; n = 3, error bars = SD.