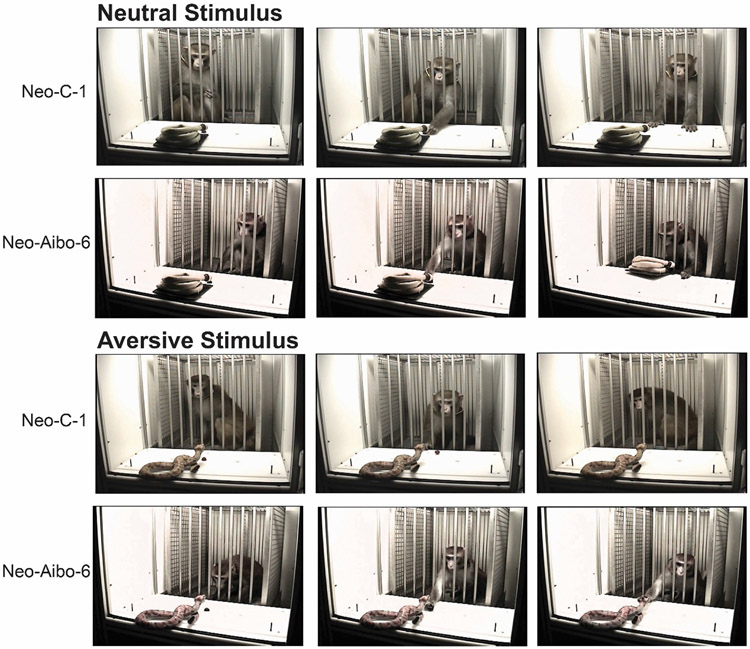
Figure 3.
Example responses toward neutral and aversive stimuli. Series of three video frames (from left to right) depicting when the stimuli is first visible, when the monkey retrieves the grape and their response to the stimulus after grape retrieval for one control male (Neo-C-1) and one neonatal amygdala lesioned male (Neo-Aibo-6). For the neutral stimulus (coiled water hose), although both monkeys are close the stimulus at the beginning and readily retrieve the grape, only the lesioned monkey manipulated the hose. For the aversive stimulus (rubber snake), the control monkey primarily remained in the back of the WGTA (first and third frames) and did a quick swiping motion to roll the grape close for retrieval. The lesioned monkey closely visually inspected and manipulated the snake (first and third frames), but unlike the control monkey, they calmly retrieved the grape similar to their neutral stimulus trial.