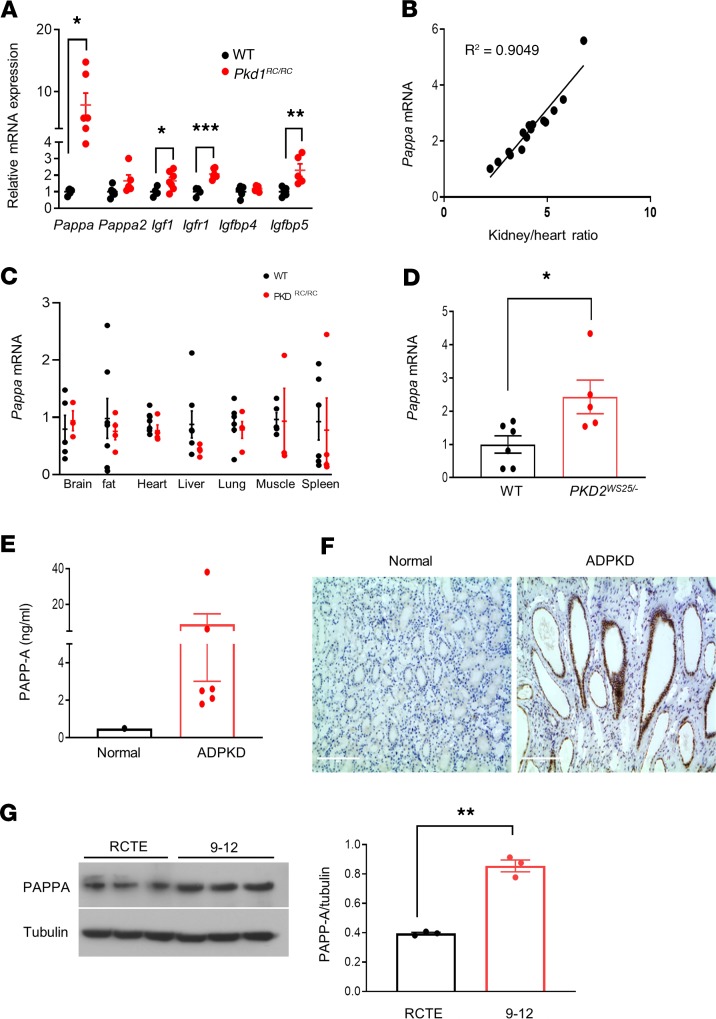
Figure 1. Upregulation of PAPP-A is a common feature in experimental and human ADPKD.
(A) Relative mRNA expression of IGF-1 pathway components in kidneys of 7.5-month-old C57BL/6J (n = 4–6) and Pkd1RC/RC mice (n = 5–7). PCR data are expressed relative to Gapdh. (B) Correlation between kidney size (total kidney weight relative to heart weight) and renal Pappa mRNA expression in Pkd1RC/RC mice (n = 15). (C) Pappa mRNA levels in various tissues of WT (n = 3–5) and Pkd1RC/RC mice (n = 4–6). (D) Pappa mRNA levels in WT (n = 6) and Pkd2WS25/– (n = 5) mouse kidneys (16 weeks old). (E) ELISA analysis of PAPP-A protein levels in human ADPKD cystic fluid (n = 6) compared with normal serum reference. (F) Immunolocalization of PAPP-A in normal and ADPKD human kidneys. (G) Western blot analysis of PAPP-A protein levels in normal human RCTE and ADPKD cystic epithelial cells (9-12); graph shows quantification relative to tubulin. Scale bars: 200 μm. Data are expressed as mean ± SEM. *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01, ***P < 0.001 by 2-tailed (for Igf1, 1-tailed) Student’s t test.