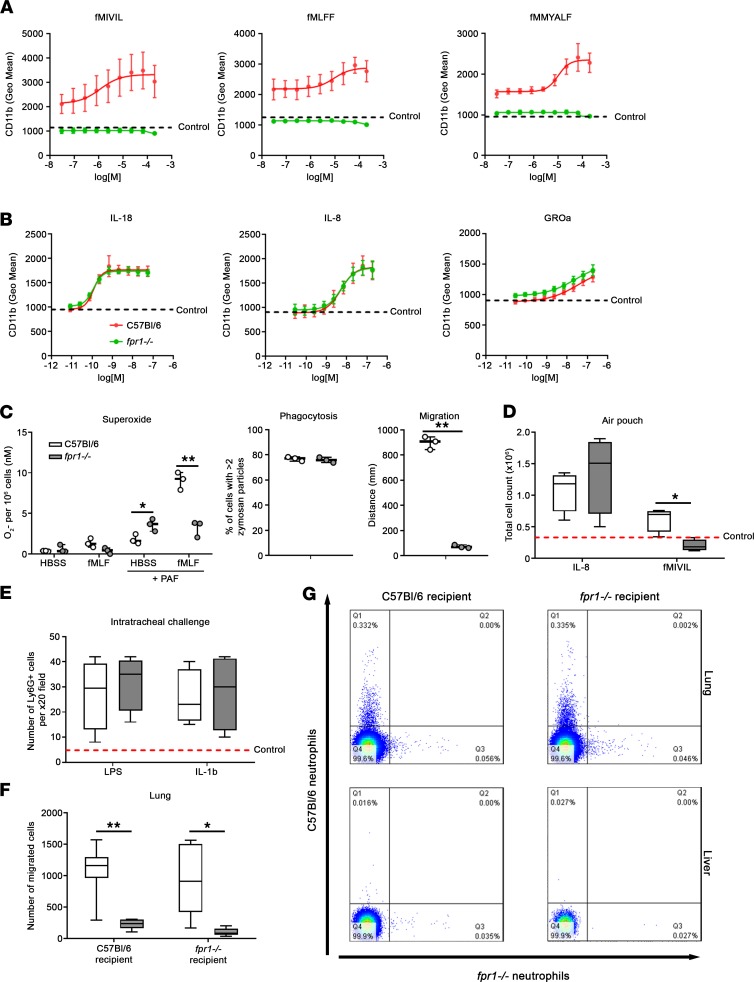
Figure 7. FPR-1 is required for effective neutrophil migration to injured lung tissue.
Bone marrow derived cells from C57BL/6 and fpr1–/– mice were stimulated with formyl peptides (fMIVIL, fMLFF, fMMYALF) (A) or IL-18, IL-8, and GROα (B) and the change in CD11b expression on neutrophils (GR1+ cells) assessed by flow cytometry. (C) Bone marrow–derived neutrophils (>95% purity) from C57BL/6 and fpr1–/– mice were assessed for their ability to release superoxide, phagocytose zymosan particles and migrate toward formyl peptides. (D) C57BL/6 and fpr1–/– mice were stimulated intrapouch for 4 hours with IL-8 (250 μM) or fMIVIL (3 μM) and total cell recruitment measured in an inflammatory subcutaneous air pouch model by flow cytometry. Dotted line indicates mean total cell influx observed for control group with carboxymethyl cellulose carrier alone. (E) C57BL/6 and fpr1–/– mice were challenged intratracheally with saline (30 μl), LPS (1 μg/mL), or IL-1β (1 μg/mL) and lung tissue harvested on day 1. Data represent the mean number of Ly6G+ cells of n = 20 randomly selected, nonoverlapping fields (original magnification, ×20) per mouse. Dotted line indicates mean number of Ly6G+ cells observed for saline-challenged mice. Bone marrow–derived neutrophils (>95% purity) were isolated from C57BL/6 and fpr1–/– mice, labeled (CFSE, C57BL/6; Violet, fpr1–/–), mixed (1:1 ratio), and injected via a single intravenous injection into recipient (C57BL/6 and fpr1–/–) mice. After transfer of cells, mice were challenged with bleomycin to induce acute pulmonary injury and culled after 2 hours. Lung (G, top) and liver homogenates (G, bottom) were analyzed by flow cytometry to quantify neutrophil migration (F and G). n = 6–7 mice per group for A–E and n = 8 mice per group for F and G. Data were analyzed using a Mann-Whitney U test and presented as box-and-whisker plots. *P < 0.05; **P < 0.01.