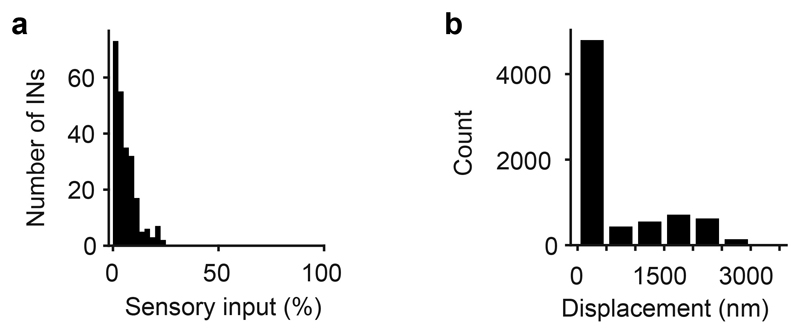
Extended Data Fig. 1. Sensory input to INs and mapping of datasets.
a, Distribution of the fraction of synaptic inputs onto INs that originated from sensory axons. The average fraction of synaptic inputs onto INs that came from sensory neurons was 5.9 ± 4.6% (mean ± s.d.). This is an upper-bound estimate because structures in EM images were classified as sensory synapses even when they were small and when synaptic features such as postsynaptic densities and vesicle clusters were ambiguous. No obvious synaptic connections were observed from OB neurons onto axon terminals of sensory neurons. b, Displacement of regions of interest (ROIs) during manual proofreading. ROIs representing somata were mapped from the EM dataset to optical image planes in each trial by an affine transformation that was determined by an iterative landmark-based procedure (Methods). Subsequently, the position of each ROI was adjusted manually on the optical image (n = 7,280 ROIs; six image planes with 11 trials each). The mean displacement (± s.d.) during manual adjustment (proofreading) was small (593 ± 833 nm), implying that automated mapping was highly reliable.