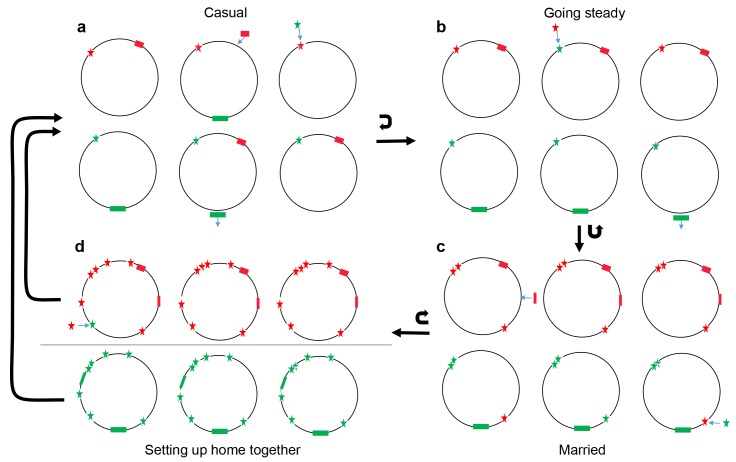
Figure 8. Conceptual model of four stages of coadaptation, analogous to human relationships.
Circles indicate bacterial strains within a population. Red and green stars indicate the two alleles of a SNP. Red and green rectangles indicate different accessory genes or genome islands. Blue arrows indicate transitions between different SNP alleles, or gain/loss of genes and genome islands. Black arrows indicate the transitions between different stages, or cycles within a stage. (a) Casual: frequent gene flow generated multiple combinations of different variants within a population. Some combinations might have high fitness but alternate combinations arise frequently due to gene flux and adaptation at individual loci. (b) Going steady: coadapted interactions, such as the SNPs (red star) and accessory gene (red rectangles), become more difficult to dislodge despite ongoing genetic exchange due to their high fitness when present in combination. (c) Married: coadapted interactions become fixed in the population and led to further co-adaptation in multiple genome regions. (d) Setting up home together: as the progressive enlargement of coadapted regions in the genome, the entire genome becomes differentiated, which prompt the barriers (horizontal line) to genetic exchange between different ecogroups.