Figure 2: Glutamatergic neurotransmission is required for GABA neuron survival.
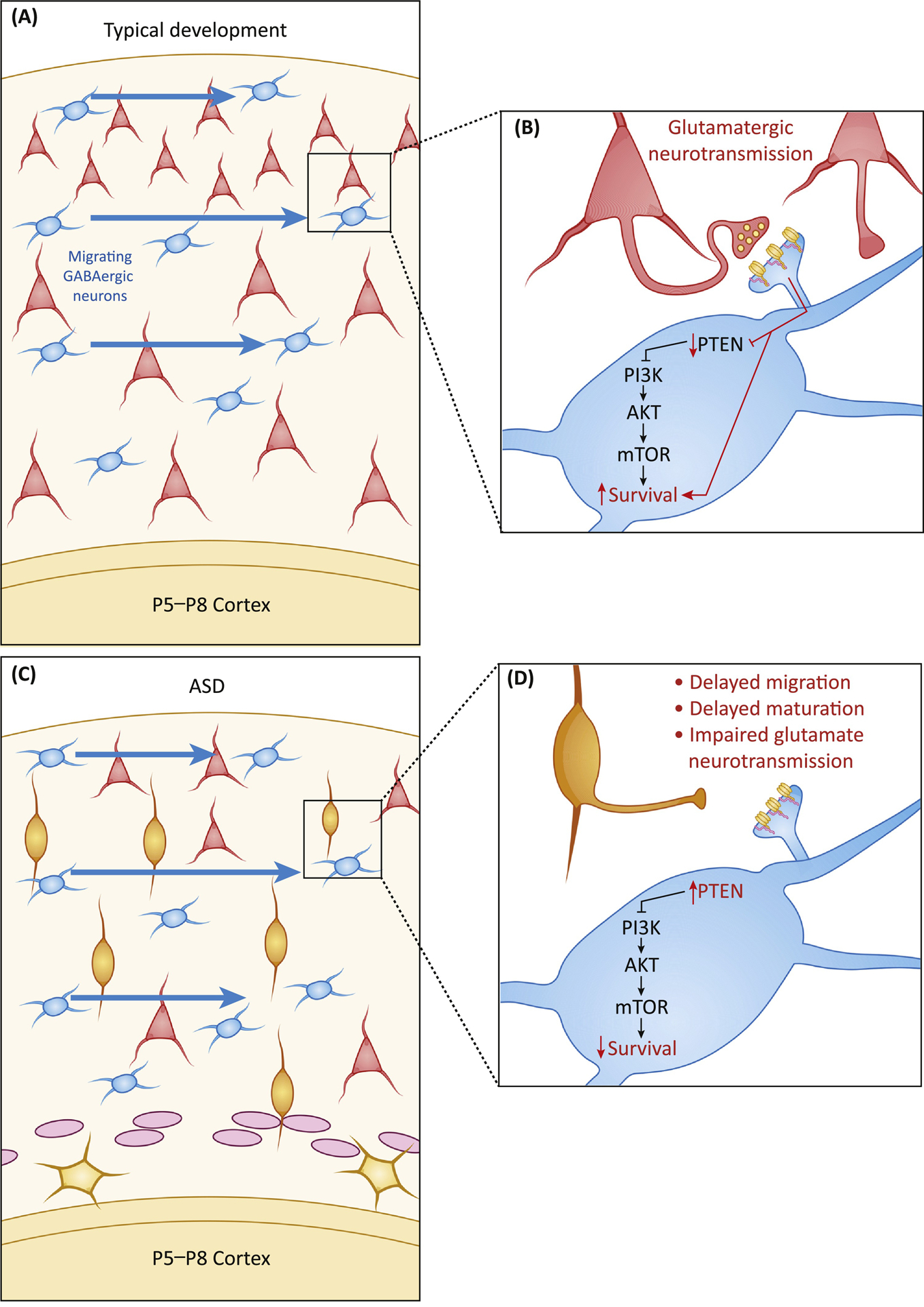
A) GABAergic neurons migrate tangentially, from their origin in the medial ganglionic eminence to their final locations in the cortex, arriving in the early postnatal period (illustration timing refers to mice; P5–8: postnatal days 5 to 8). B) Upon arrival, GABAergic neurons must form excitatory glutamatergic synapses with local cortical neurons. Transmission through these synapses promotes survival in a PTEN-dependent manner. C) If the timing of excitatory neuron migration is disrupted by an ASD-linked risk factor, local cortical neurons may not have yet reached their final position, or they may be too immature to form functional synapses. D) If local pyramidal cells are unable to form synapses with GABAergic neurons, PTEN activity increases, leading to reduced mTOR pathway activation and increased apoptosis of GABAergic neurons.
