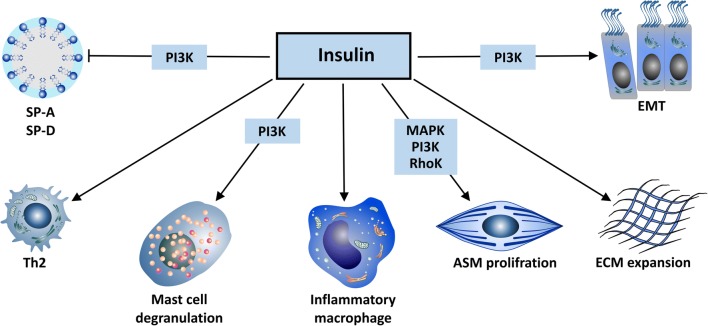
Fig. 3.
Schematic representation of insulin effects on the lung. Insulin inhibits surfactant protein A (SP-A) and surfactant protein D (SP-D) production via a phosphoinositide-3–kinases (PI3K) pathway. Insulin inhibits the proliferation of T helper cell type 1 (Th1) and shifts T cells towards a T helper cell type 2 (Th2)-type response. Insulin promotes mast cell survival, degranulation and histamine release via a PI3K pathway and activates pulmonary inflammatory macrophages. Insulin proliferates and contracts airway smooth muscle cells (ASMs) via mitogen-activated protein kinase (MAPK), Rho kinase and PI3K pathways. Insulin increases the deposition of extracellular matrix (ECM) in the lung and promotes epithelial-mesenchymal transition (EMT) and fibrosis via the PI3K/protein kinase B β-catenin pathway