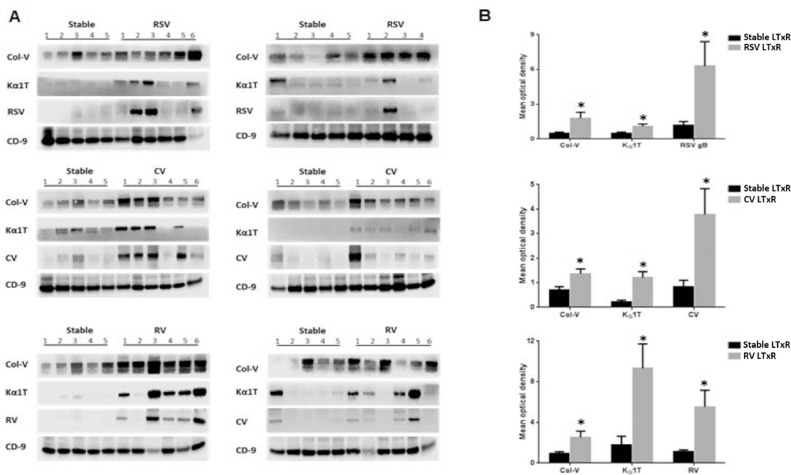
Figure 3.
Lung-associated SAgs and viral antigens were demonstrable in exosomes isolated from patients with RVI. Exosomes isolated from serum samples of patients with RVI and from stable LTxRs were used to detect the presence of lung-associated SAgs and viral antigens using immunoblot. The results showed a significant increase in lung-associated antigens and viral antigens. (A) RSV (n = 10), coronavirus (n = 12), and rhinovirus (n = 12) in respective patients with viral infection compared with stable LTxRs (n = 30). (B) Graphical representation shows the optical density of lung-associated SAgs and viral antigens measured in RVI and stable LTxRs using ImageJ software. Optical density of lung SAgs and viral antigens were normalized with exosomes specific marker CD9. The presence of lung SAgs and viral antigens in the exosomes was compared between the cohorts using Mann–Whitney test. Asterisk indicates statistically significant. Col-V, collagen-V; CV, coronavirus; Kα1T, K-alpha-1 tubulin; LTxR, lung transplant recipient; RSV, respiratory syncytial virus; RV, rhinovirus; RVI, respiratory viral infection; SAg, self-antigen.