Figure 5. PPI networks formed by ASD-risk genes.
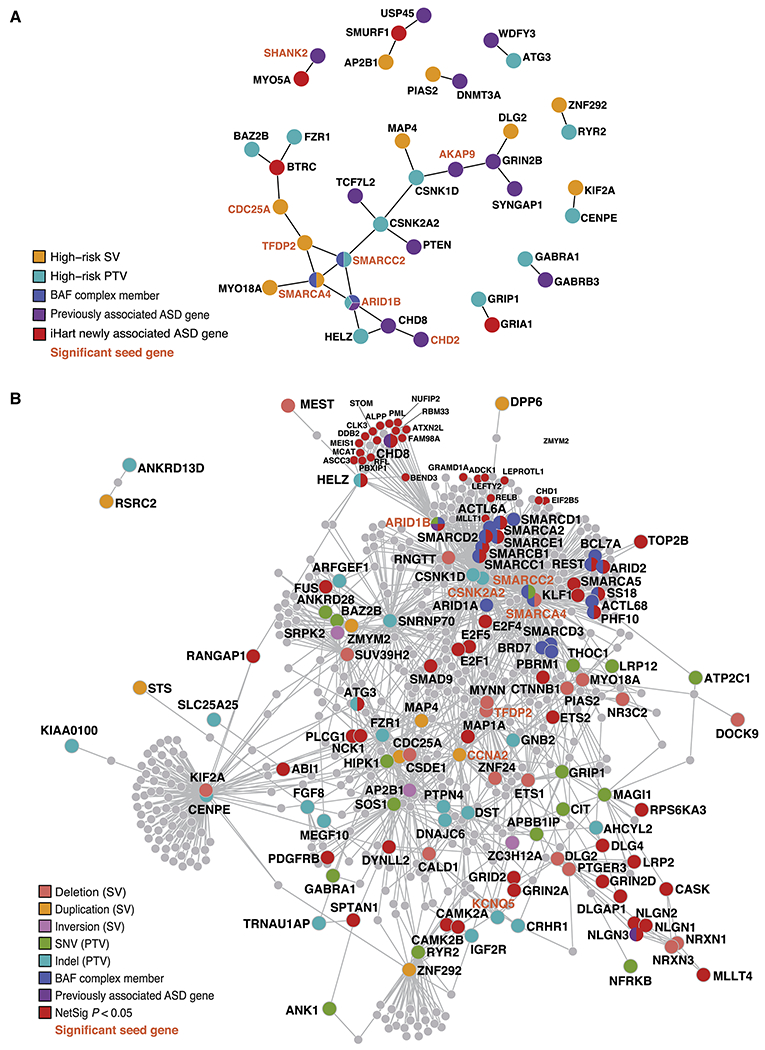
(A,B) Proteins encoded by previously known ASD-risk genes (Sanders et al., 2015) are shown in purple, those belonging to the BAF complex are blue, and those belonging to more than one category are shown with all colors that apply. Gene labels for significant seed genes are bold and orange. (A) Direct PPI network formed by constrained genes harboring high-risk inherited variants (98 genes) and ASD-risk genes identified in the TADA mega-analysis (69 genes, FDR<0.1). The direct PPI network formed by these 165 unique genes is significant for three connectivity metrics: the direct edges count (P=0.036), the seed direct degrees mean (P=0.046), and the CI degrees mean (P=0.005). Proteins encoded by a gene with a high-risk inherited SV are shown in gold, those with PTVs are teal, and those that are a newly identified ASD-risk gene by the iHART TADA mega analysis are shown in red. (B) Indirect PPI networks seeded by genes harboring high-risk inherited variants (98 genes). Proteins are colored according to the variant class identified and NetSig significant genes (P<0.05) are shown in red.
