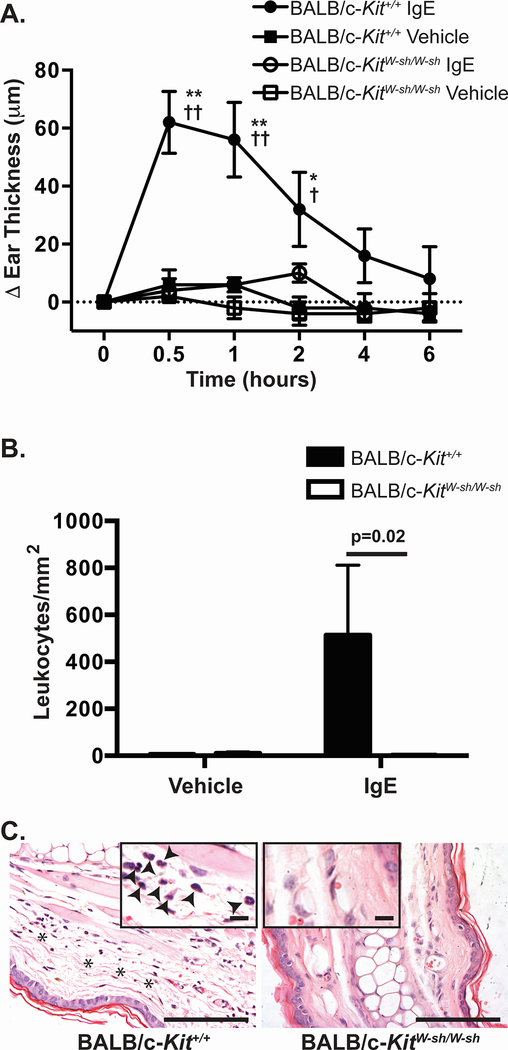
Figure 3.
IgE-dependent passive cutaneous anaphylaxis is diminished in BALB/c-KitW-sh/W-sh mice. Mice were injected i.d. with vehicle (saline) in one ear and anti-DNP-IgE in the opposite ear. 24 h later, mice were challenged i.v. with DNP-HSA. A. Ear swelling was measured at the time intervals indicated. B, C. Mice were killed 6 h after injection of DNP-HSA and leukocytes present in the dermis were counted (B) in hematoxylin & eosin (H&E)-stained sections of ear pinnae at the sites which had been injected with saline or anti-DNP-IgE (C). C. Histology of the site which had been injected with anti-DNP-IgE shows edema (indicated with asterisks) and the presence of leukocytes in the dermis (solid arrowheads in the inset) in sections from wild type BALB/c-Kit+/+ mice but not in those of BALB/c-KitW-sh/W-sh mice. N=5 mice per group. Mean values are shown ± s.e.m. for one of two independent experiments, each of which gave similar results. ** p<0.0001 and * p<0.001 for BALB/c-Kit+/+ IgE vs. BALB/c-Kit+/+ vehicle; †† p<0.0001 and † p<0.05 for BALB/c-Kit+/+ IgE vs. BALB/c-KitW-sh/W-sh IgE as determined by 2-way ANOVA. Scale bars in C indicate 100 μm and, for the insets, 13 μm.