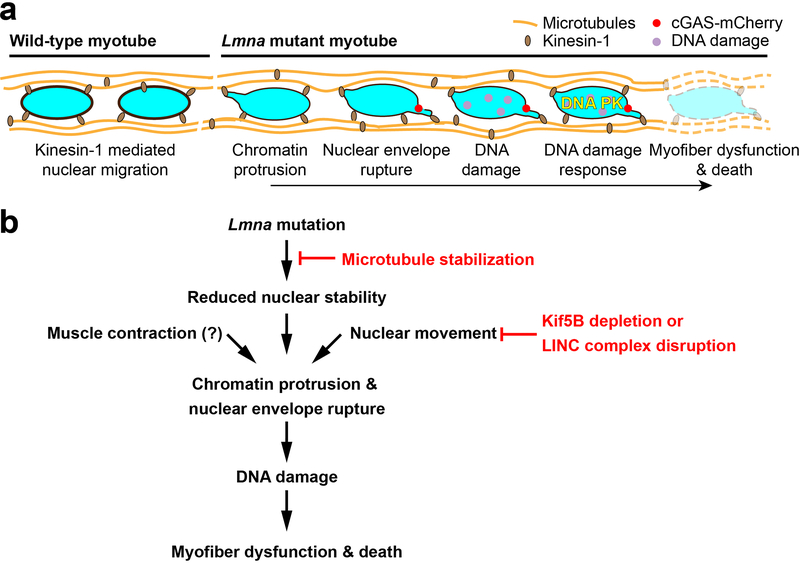
Extended Data Fig. 10. Proposed mechanism by which Lmna mutations result in myofiber dysfunction and death.
Kinesin-1 motor proteins spread myonuclei along the myotubes axis during differentiation. In Lmna mutant cells, which have mechanically weaker nuclei, the localized forces associated with nuclear migration cause chromatin protrusion and NE ruptures. This mechanically induced nuclear damage results in DNA damage, detected by H2AX foci, and activation of DNA damage response pathways, which leads to decline in myofiber health and cell death. (b) Schematic flow chart delineating the steps described in panel a, along with interventions explored in this work. Stabilizing microtubules surrounding the myonuclei reinforces the Lmna mutant nuclei and prevents chromatin protrusions and NE ruptures. Inhibiting nuclear movement by Kif5b depletions similarly prevents nuclear damage. Muscle contractions may also contribute to nuclear damage in vivo.