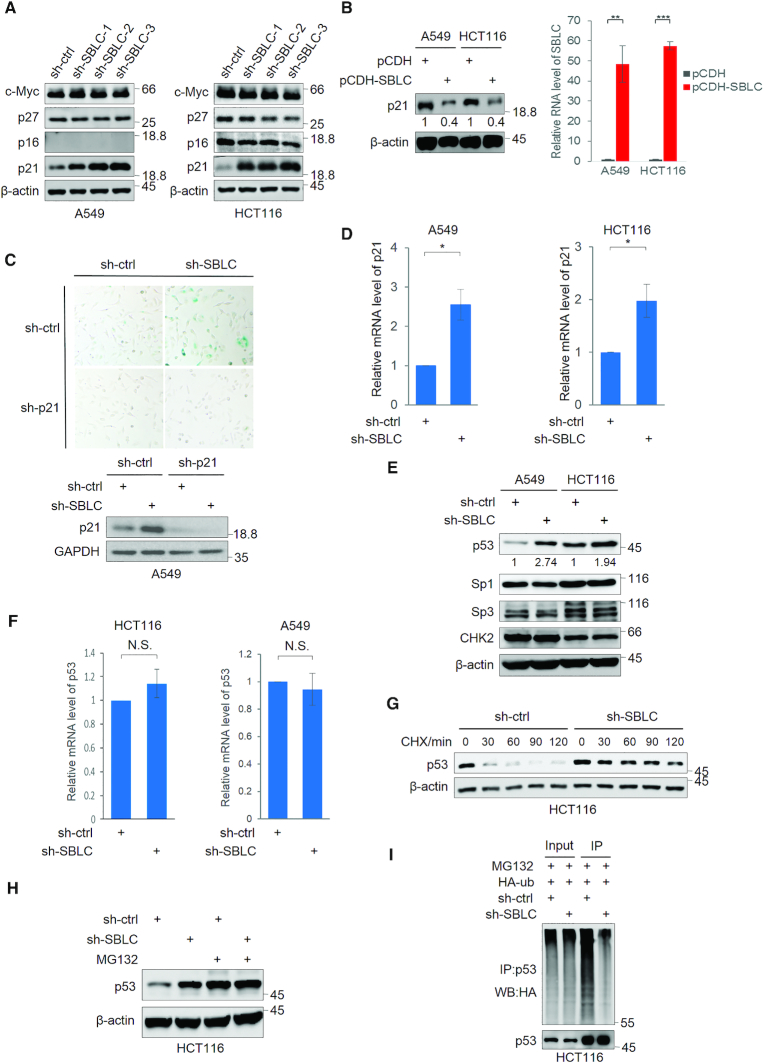
Figure 3.
SBLC acts to repress p21 expression via transcriptional control via p53. Western blotting for c-Myc, p27, p16 and p21 in A549 and HCT116 cells after transduction with sh-ctrl or independent shRNAs against SBLC (A) or p21 levels after transfection of SBLC (pCDH-SBLC) or empty vector (pCDH). Overexpression efficiency was assessed by qPCR (B). β-actin served as a loading control throughout. (C) SA-β-galactosidase staining (top) and western blotting for p21/GAPDH (bottom) in A549 cells after transduction with sh-ctrl or sh-SBLC#3 in combination with p21 shRNA (sh-p21) for 24 h. (D) qPCR measurement of p21 mRNA in A549 cells. (E) Western blotting for p53, Sp3, Sp1 and Chk2 in A549 and HCT116 cells after transduction with sh-ctrl or sh-SBLC. Relative p53 levels were estimated using densitometry. (F) qPCR analysis of p53 mRNA levels in A549 and HCT116 cells. (G) Western blot against p21 in A549 cells treated with cycloheximide. (H) Western blot against p53 in HCT116 cells following 6 h pre-treatment with 20 μM MG132. (I) Western blotting against HA in cell lysates and p53 IPs from HCT116 transfected with HA-ubiquitin. (A–I) Results are representative of three independent experiments. Values are mean ± SEM. *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01, ***P < 0.001, Student’s t-test.