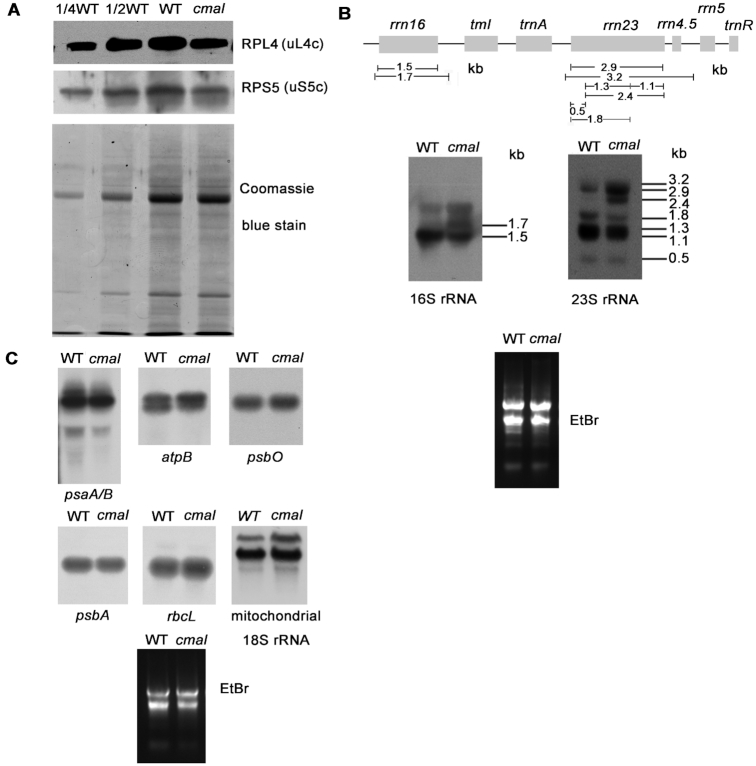
Figure 4.
Accumulation of chloroplast ribosomes in cmal. (A) Immunoblot analysis of chloroplast ribosomal proteins of 3-week-old cmal and WT plants. Total leaf protein (20 μg or the indicated dilution of WT samples) was analyzed by probing the immmunoblots with antibodies against RPL4 and RPS5. The Coomassie blue-stained blot at the bottom serves as a loading control. RPS5 and RPL4 are also renamed as uS5c and uL4c, respectively, according to the new nomenclature of ribosomal proteins (53) (https://bangroup.ethz.ch/research/nomenclature-of-ribosomal-proteins.html). (B) Levels of 16S and 23S rRNAs in 4-week-old cmal and WT plants. Total RNA from Arabidopsis leaves was analyzed using an RNA gel-blot hybridization with specific probes for 16S and 23S rRNA. The diagram of the rRNA operon and locations and sizes of distinct forms of rRNA species observed by RNA gel blotting are shown on the top. The gel was stained with ethidium bromide (EtBr) to visualize the rRNA, and was used as a loading control. (C) The abundance of chloroplast-encoded mRNAs and mitochondrial 18S rRNA was assayed using RNA gel-blot hybridizations as performed in (B).