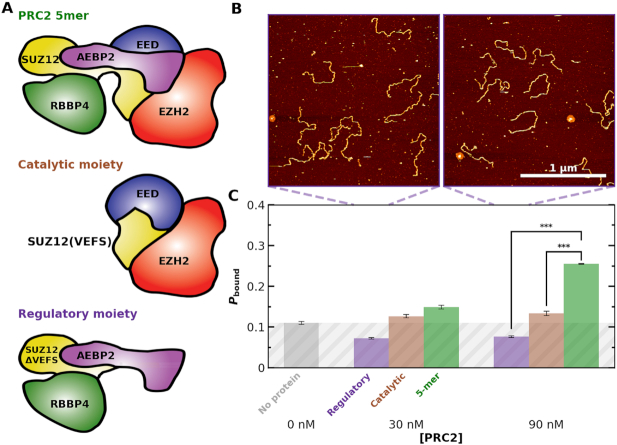
Figure 5.
PRC2 binding depends on PRC2 complex composition. (A) Cartoons illustrating the measured PRC2 moieties. (top) The ‘5mer’ complex consists of EZH2 (red), EED (blue), SUZ12 (yellow), AEBP2 (purple) and RBBP4 (green). (middle) The catalytic moiety of PRC2 consists of EZH2, the VEFS domain of SUZ12, and EED with the 81 N-terminal amino acids deleted. (bottom) The regulatory moiety of PRC2 consists of SUZ12ΔVEFS, AEBP2, and RBBP4. (B) Representative 2 × 2 μm2 images at 30 and 90 nM concentrations of the regulatory moiety of PRC2. (C) Probability of observing a PRC2-DNA complex (Pbound) as a function of PRC2 concentration for the regulatory (purple), catalytic (gray) and 5-mer (green) moieties of PRC2. Concentrations below the 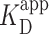 were used to enhance the signal. The triple asterisk represents a statistical significance of P < 0.001. The average Nmolecules at 0, 30 and 90 nM were greater than 80, 90 and 200, respectively, and the error bars represent the standard error in the mean. Gray shading indicates the false positive rate, based on the no added PRC2 control.
were used to enhance the signal. The triple asterisk represents a statistical significance of P < 0.001. The average Nmolecules at 0, 30 and 90 nM were greater than 80, 90 and 200, respectively, and the error bars represent the standard error in the mean. Gray shading indicates the false positive rate, based on the no added PRC2 control.