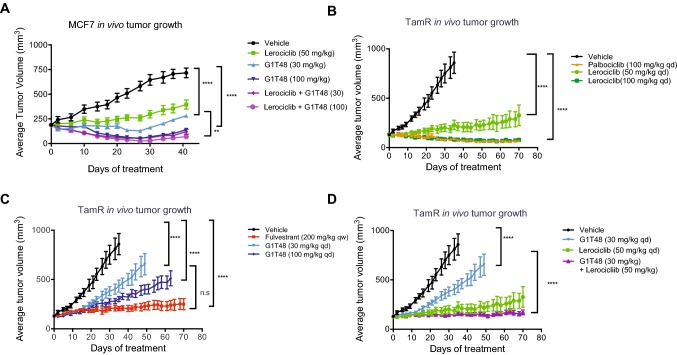
Fig. 5.
Combination strategy of G1T48 and the CDK4/6 inhibitor lerociclib inhibit estrogen-dependent and tamoxifen-resistant (TamR) breast cancer xenograft models in vivo a Ovariectomized estrogen-treated female nu/nu mice bearing MCF7 xenograft tumors were randomized to treatment with vehicle, lerociclib (50 mg/kg) or G1T48 (30 or 100 mg/kg), alone or together, p.o. daily for 28 days. 2-way ANOVA comparison of average tumor volumes throughout treatment, followed by Bonferroni multiple comparison test, indicated significant tumor growth inhibition by all treatments, as well as increased response to the combination of G1T48 (30 mg/kg) and lerociclib (50 mg/kg). Error bars represent SEM. b–d Ovariectomized tamoxifen-treated female nu/nu mice bearing TamR xenograft were randomized to treatment with vehicle, palbociclib (100 mg/kg), lerociclib (50 or 100 mg/kg) (b), fulvestrant (200 mg/kg), or G1T48 (30 or 100 mg/kg) (c), with lerociclib and G1T48 being tested alone and in combination (d), p.o. daily for 28 days. 2-way ANOVA comparison of average tumor volumes throughout treatment, followed by Bonferroni multiple comparison test, indicated significant tumor growth inhibition by all treatments, as well as increased response to the combination of G1T48 (30 mg/kg) and lerociclib. Error bars represent SEM