Figure 3.
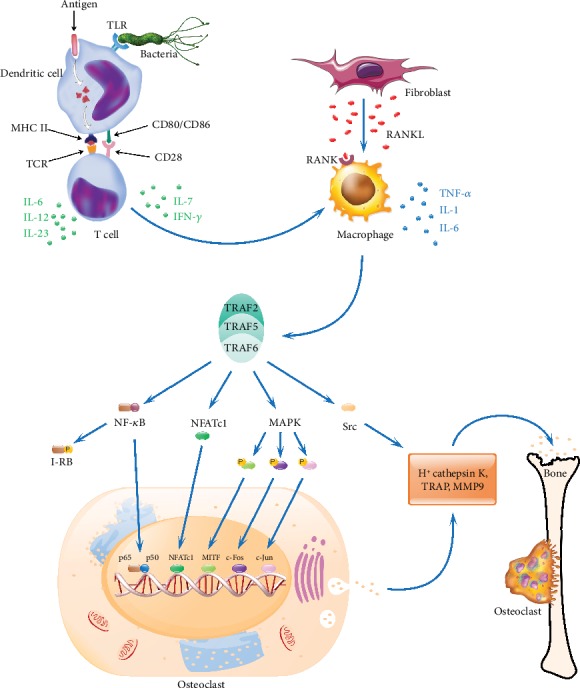
Signaling pathways in osteoclast activation. During RA pathogenesis, antigen-presenting cells after uptake of an autoantigen or pathogenic molecules process and present antigenic determinants on their cell surface in conjunction with arthritis-permissible HLA/MHC class II molecules, which activate differentiation of T cells into different subphenotypes. The activated T cells secrete various cytokines like IL-6, IL-7, IL-10, IL-12, IL-17, IL-23, and IFN-γ. These cytokines modulate macrophages to secrete various pro- and/or anti-inflammatory cytokines and other inflammatory mediators. Upon exposure to the inflammatory cytokines, fibroblast-like synoviocytes express RANKL, which binds with its receptor (RANK) present on the cell surface of activated macrophages initiating the RANK/RANKL pathway through TRAF 2, 5, and 6 proteins, which leads to the activation of downstream NF-κB, MAPK, NFATc1, and Src signaling cascades. These factors after translocation initiate the expression of genes like TRAP, CtsK, and MMP-9 in the nucleus, which promote osteoclastogenesis and bone resorption. TLR: toll-like receptor; TCR: T cell receptor; CtsK: cathepsin K; I-κB: inhibitor of the NF-κB transcription factor; IL: interleukin; IFN-γ: interferon gamma; MAPK: mitogen-activated protein kinase; MHC II: major histocompatibility complex II; MITF: microphthalmia-associated transcription factor; MMP 9: matrix metalloproteinase 9; NFATc1: nuclear factor of activated T cells, calcineurin-dependent 1; NF-κB: nuclear factor kappa B; p50 and p65: REL-associated proteins (also called NF-κB1 and RelA) involved in NF-κB heterodimer formation and nuclear translocation and activation; RANK: receptor activator of nuclear factor-κB; RANKL: receptor activator of nuclear factor κB ligand; Src: intracellular non-receptor tyrosine kinase; TRAF: TNF receptor-associated factor; TRAP: tartrate-resistant acid phosphatase. c-Jun and c-Fos form the early response transcription factor, AP-1.
