Fig. 3.
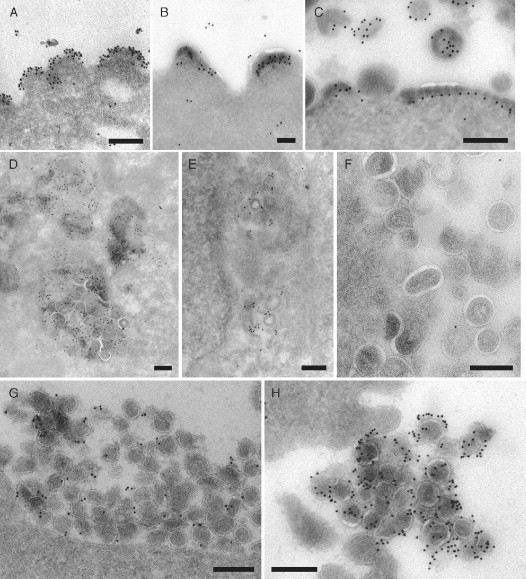
Analysis of SIV assembly by immunolabeling of cryosections. (A, B, and C) SIV Gag‐GFP VLPs budding from the surface of transfected COS cells. The buds were immunolabeled with mouse monoclonal antibodies against SIV MA (mAb KK59 in A) or CA (mAb KK64 in B, antibodies provided by Dr. K. Kent through the NIBSC Centralised Facility for AIDS Reagents, Potters Bar, UK) and a rabbit anti‐mouse IgG‐bridging antibody (Dako UK Limited, Ely, UK), or with a rabbit polyclonal antiserum recognizing GFP (C; Living Colors™ peptide antibody, Clontech Laboratories, Inc., Mountain View, CA, USA). All antibodies were detected with 10‐nm PAG. (D, E, and F) COS cells expressing SIV Gag and assembling VLPs in intracellular vacuoles resembling multivesicular bodies were immunolabeled with mouse monoclonal antibodies against CD63 (Fraile‐Ramos et al., 2001) or against LBPA (Kobayashi et al., 1998, provided by Dr. J. Gruenberg, University of Geneva, Switzerland) and 10‐nm PAG. The LBPA antibody labels intracellular (E), but not cell surface (F) VLPs. (G and H) Virus particles at the surface of CEMx174 cells chronically infected with SIVmac239 expressing an Env glycoprotein with a long cytoplasmic domain (G) or SIVmac239/251T with a cytoplasmically truncated Env protein (H) were stained with an antibody against SIV Env SU (Edinger et al., 2000, provided by Dr. R. W. Doms, University of Pennsylvania, Philadelphia) and 10‐nm PAG. The immunolabeling suggests that these two virus strains incorporate different amounts of the Env protein. PAG reagents were purchased from The Cell Microscopy Center, University Medical Center, Utrecht, The Netherlands. Scale bars = 200 nm.
