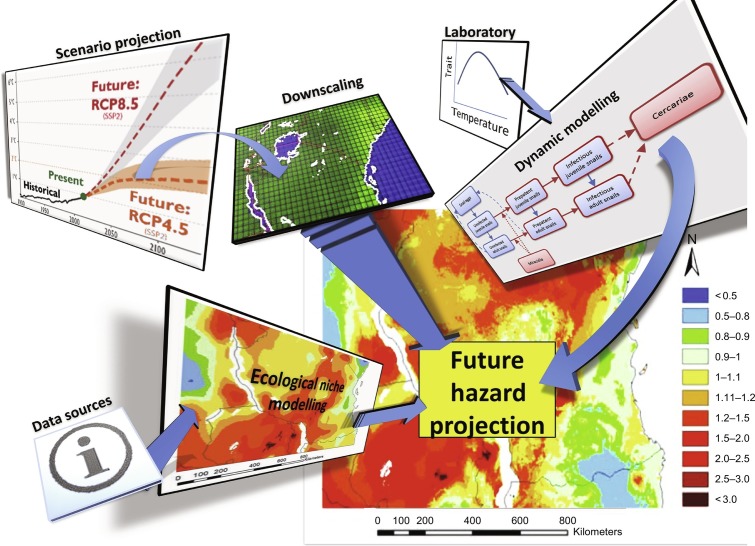
Fig. 7.
Illustration of the steps taken to map future transmission potential of S. mansoni in East Africa, combining functional trait knowledge on the relationship between temperature and Biomphalaria fecundity with dynamic agent-based models, downscaled climate projections and ecological niche modelling. The results of combining the outputs of these models and experiments resulted in a high-resolution hazard map which was then used to underpin a risk map that incorporated a vulnerability layer as observable in the Healthy Futures Atlas.
Elements of the figure reproduced from McCreesh, N., Booth, M., 2014. The effect of increasing water temperatures on Schistosoma mansoni transmission and Biomphalaria pfeifferi population dynamics: an agent-based modelling study. PLoS ONE 9 (7). doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0101462; Stensgaard, A.-S., et al., 2016. Combining process-based and correlative models improves predictions of climate change effects on Schistosoma mansoni transmission in eastern Africa. Geospatial Health 11 (1 Suppl), 406. doi: 10.4081/gh.2016.406.