Fig. 4.
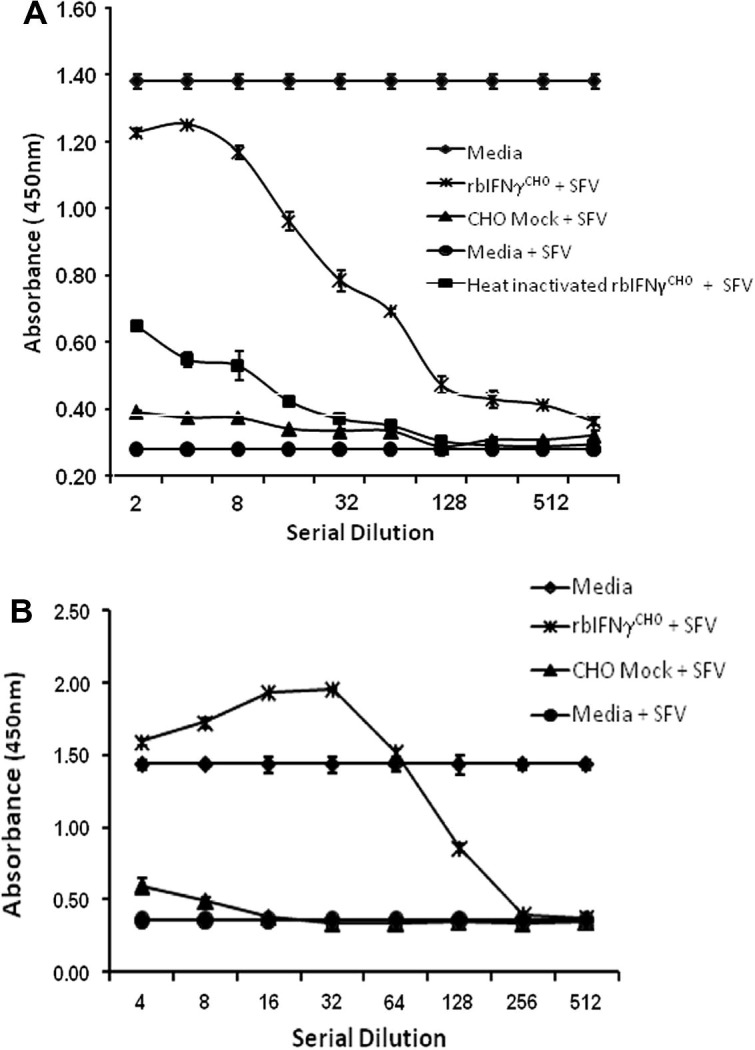
Recombinant bat IFNγ displays antiviral activity against Semliki forest virus in P. alecto and T. brasiliensis cell lines. Cells were pre-treated overnight with serial dilutions of supernatants from CHO cells transfected with pCI plasmid containing bat IFNγ (rbIFNγCHO) or pCI vector alone (CHO mock). Cells were then infected with SFV for 48 h. Assay controls included replicates pre-treated with media alone and cultured for a further 48 h either infected (media + SFV) or uninfected (media). Cell death due to viral infection was determined by a colorimetric assay using the viral dye neutral red. Pre-treatment of (A) P. alecto PaKiT02 cells or (B) T. brasiliensis Tb1-Lu cells with rbIFNγCHO protects from SFV infection in a dose dependent manner. Data are mean values of triplicates, and the error bars represent SEs.
