Fig. 6.
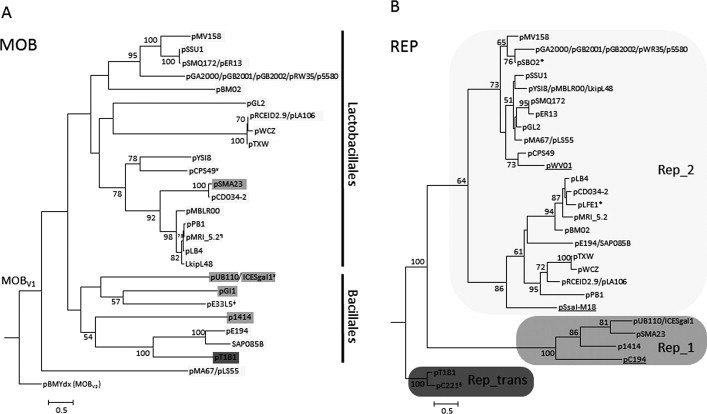
Phylogeny of the Rep and Mob (MOBV1) proteins of relevant RCR-plasmids. Representative RCR plasmids and MOBV1 elements included in Supplementary Table S2 were used to trace the evolutionary relationships of their relaxase and replication initiation proteins. The homologs were aligned using MUSCLE (Edgar, 2004). The phylogenetic reconstruction was carried out by maximum likelihood (ML), using RAxML version 7.2.7 (Stamatakis, 2006). 100 ML trees were executed using the JTTGAMMA model. 1000 bootstrap trees were then inferred to obtain the confidence values for each node of the best ML tree. Only bootstrap values >50% are indicated. (A) Phylogenetic tree of the N-terminal 300 residues of MOBV1 relaxases. Each plasmid is shadowed in gray according to the RCR initiator subgroup as indicated in the legend of panel B. ≠Indicates an exceptional MOBV1 plasmid, pE33L5, which does not encode an RCR initiator but a HTH_36 (PF13730) replication initiation protein. Vertical bars delimit clades for which most of their members are hosted either in Lactobacillales or in Bacillales. ¥Indicates an element not hosted in the taxonomic order indicated by the bars. ¶Indicates that plasmid pMRI_5.2 also encodes a Rep_1 RCR initiator. (B) Phylogenetic tree of the RCR initiators. Plasmids pT181 and pC221 were used as outgroups. A gray color palette was used to indicate clades containing different RCR initiators families: Rep_1 (PF01446) and Rep_2 (PF01719), as well as the Rep_trans (PF02486) used to root the tree. ∗According to their GenBank annotated sequences, plasmids pSBO2 and pLFE1 encode truncated MOBV relaxases and thus were not included in the MOB phylogeny, neither were the underlined plasmids (pWV01, pSsal-M18 and pC194) since they do not encode relaxases. §pC221 is a mobilizable RCR plasmid, but it encodes a MOBP7 instead of a MOBV relaxase.
