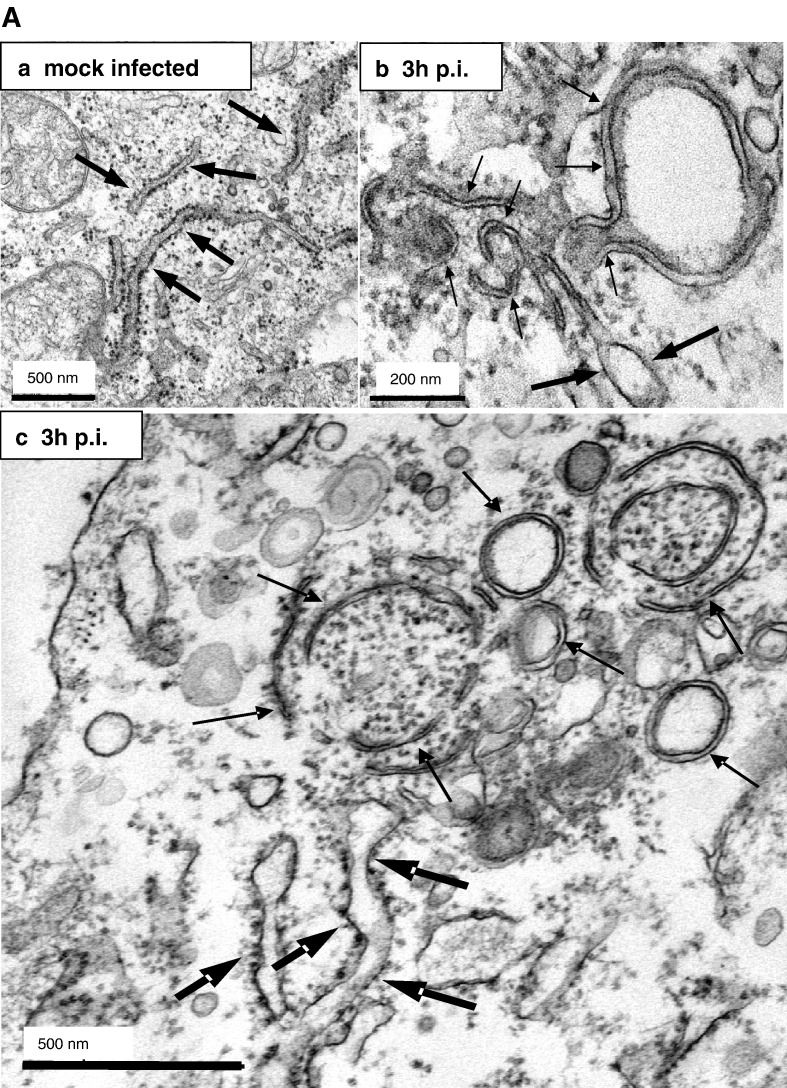
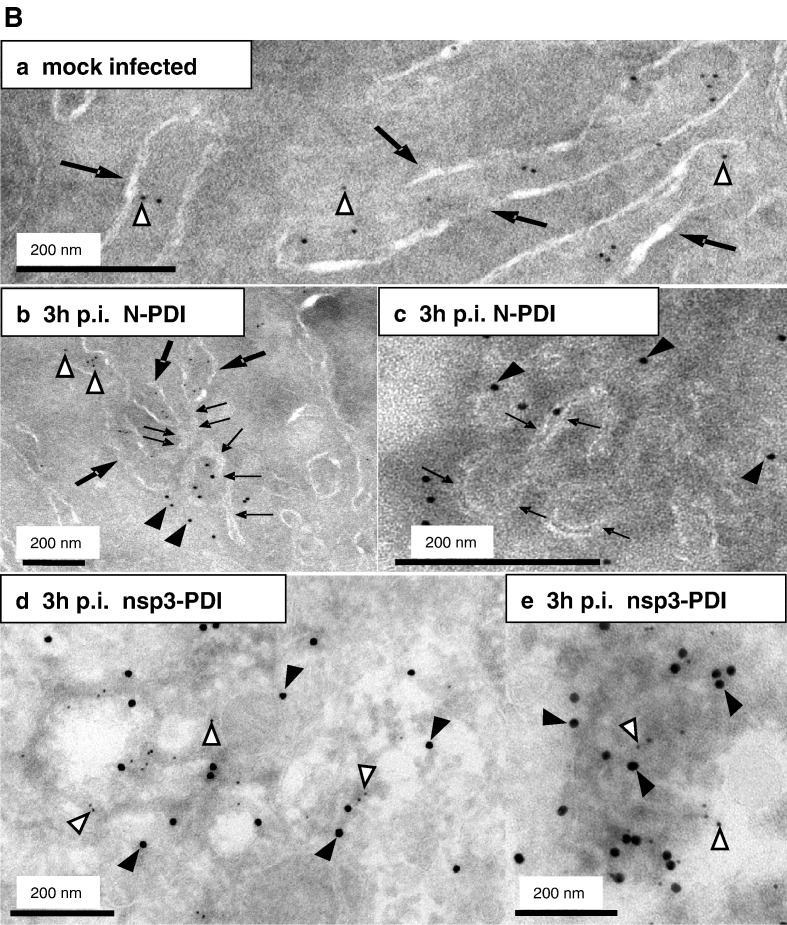
Fig. 5.
Membrane tubules within the SARS-CoV replication sites are derived from ER membranes. A) Vero cells were mock-infected (a) or infected with SARS-CoV (MOI of 10) for 3 h (b, c), fixed and analyzed by standard EM. ER cisternae are marked with large arrows, whereas the double membrane vesicles and the membrane tubules characteristic for the putative replication sites are highlighted with small arrows. Scale bars represent 200 nm or 500 nm as indicated. B) Vero cells were mock-infected (a) or infected with SARS-CoV (MOI of 10) for 3 h (b–e), fixed and analyzed by cryo-iEM. Cells were labeled with antibodies directed against SARS-CoV N (a–c, 10 nm gold, filled arrowheads) or SARS-CoV nsp3 (d–e, 15 nm gold, filled arrowheads) and PDI as a marker for ER (a–e, 5 nm gold, open arrowheads). Panel B c and e show putative replication complexes in a higher magnification. PDI labeling surrounded the N assembly in c but is not visible in this cutout. ER cisternae are marked with large arrows (a, b) and small arrows delineate membrane tubules characteristic for the putative replication sites (b, c). Scale bars represent 200 nm.