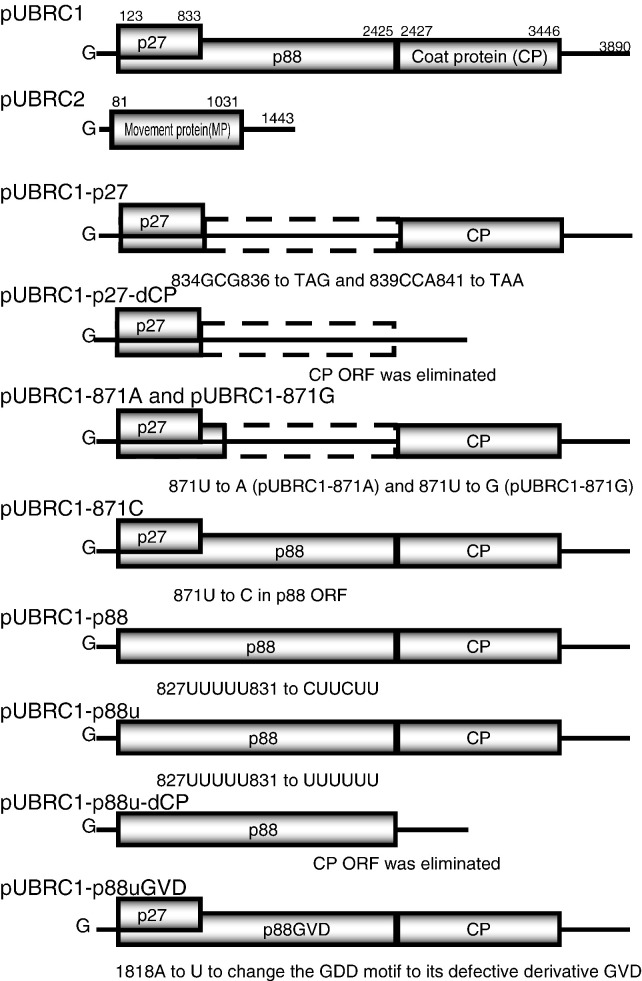
Fig. 1.
Schematic representation of wild-type RCNMV RNA 1 and 2 (pUBRC1 and pUBRC2, respectively) and mutants derived from RNA 1 (referred to as the names of plasmids). These viral RNAs had extra G residue at the 5′ end. The viral RNA was initially synthesized in vivo from the 35S promoter of CaMV, and was cleaved by the ribozyme of satellite Tobacco ringspot virus to generate the appropriate 3′ end. Individual sites of the introduced mutations were explained and indicated by open triangles.