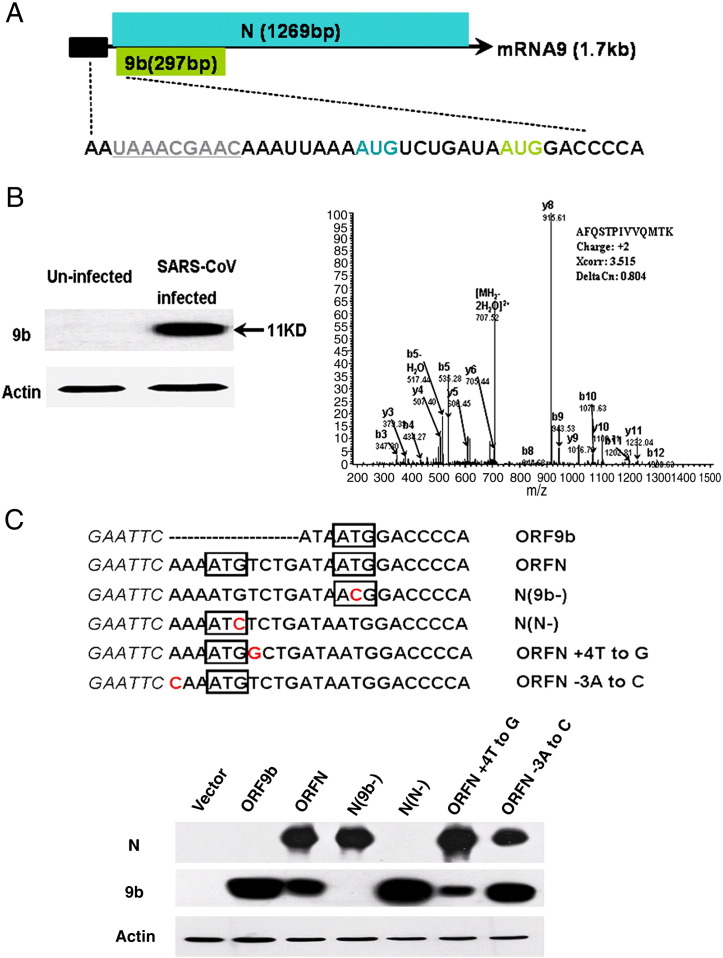
Fig. 1.
Expression of 9b protein from mRNA9. (A) SARS-CoV mRNA9 organization. ORFN, ORF9b, frameshift and transcription-regulating sequence (TRS), are shown. Black box represents RNA leading sequence. ORFN is highlighted in blue, while ORF9b is shown in an enlarged representation highlighted in green. TRS sequence is marked by underlines and in grey. Start codon of ORFN and 9b are shown in corresponding colors, adapted from (Meier et al., 2006, Thiel et al., 2003). (B) Left. 11 kDa 9b protein was detected in SARS infected FRhK-4 cells by anti-9b monoclonal antibody, but not in uninfected cells. β-actin was detected in both infected and uninfected cells. Right. 9b protein was immunoprecipitated by anti-9b polyclonal antibody from SARS infected FRhK-4 cell lysates in RIPA buffer, the mass spectrometry analysis of the corresponding gel slices detected a specific peptide that represents 9b protein. (C) Translation of ORF9b by leaky ribosomal scanning. Schematic diagram of cDNA constructs is shown (upper panel). Wild-type ORF9b sequence (ORF9b), wild-type N gene sequence (ORFN), a point mutation eliminating 9b initiation codon in ORFN sequence (N(9b−)), a point mutation eliminating N initiation codon (N(N−)), an optimal Kozak context around the ORFN initiation codon (ORFN + 4T to G), and a weaker Kozak context around the ORFN initiation codon (ORFN − 3A to C). 293T cells were transfected with plasmids encoding the indicated cDNAs and analyzed by Western blot with both anti-N and anti-9b monoclonal antibodies for each sample. β-actin was detected by actin specific polyclonal antibody.