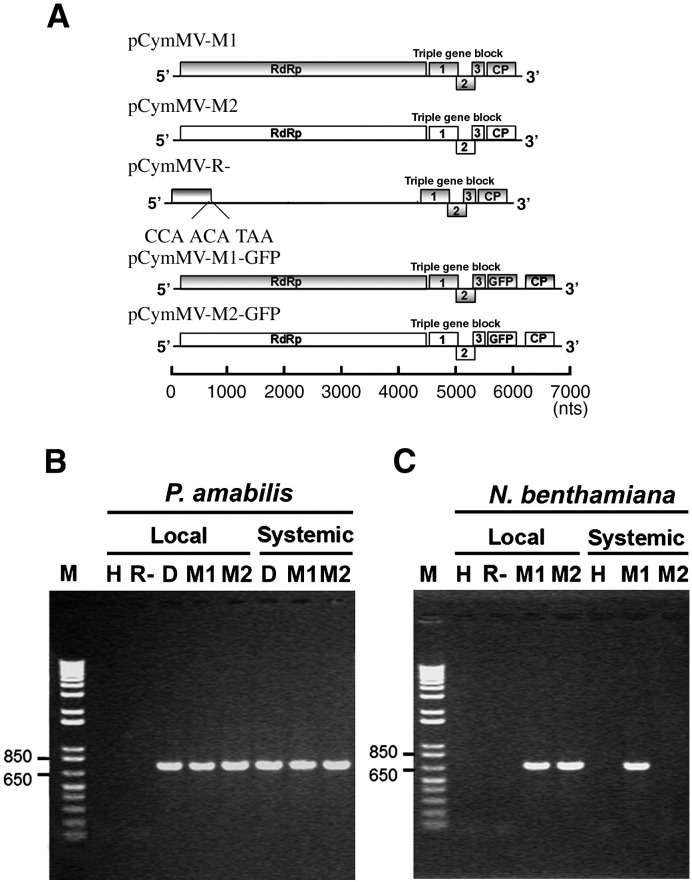
Fig. 1.
Schematic representation of CymMV cDNA infectious clones (A) and detection of CymMV in infected Phalaenopsis amabilis (B) and Nicotiana benthamiana (C) by RT-PCR. (A) Rectangles represent open reading frames encoded by CymMV genomic RNA. RNA-dependent RNA polymerase (RdRp), triple gene block ORFs 1, 2, and 3, capsid protein (CP) and green fluorescent protein (GFP). The mutated sequences in pCymMV-R- are indicated by bold letters. Scale bar, in nucleotides, is shown at the bottom. P. amabilis var. formosa (B) and N. benthamiana (C) inoculated with buffer (H), pCymMV-R- transcripts (R-), pCymMV-M1 transcripts (M1) and pCymMV-M2 transcripts (M2), with CymMV-infected Phalaenopsis used as a positive control (D). Total nucleic acids were extracted from CymMV-inoculated and upper leaves distal from the inoculation point, and CymMV was detected by RT-PCR. pCymMV-R- is a replication-incompetent clone used as a negative control (see Materials and Methods). Numbers at the left correspond to positions of marker DNAs (M) (sizes in 1000 base pairs).