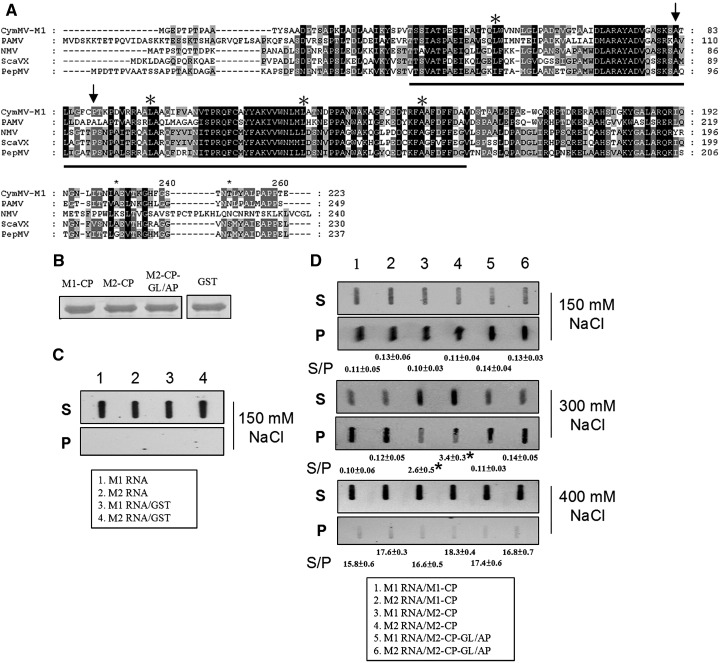
Fig. 7.
The amino acid sequence alignment of predicted RNA binding domain of potexvirus CPs and slot-blot detection of biotin-labeled CymMV RNAs. (A) The amino acid sequence alignment of predicted RNA binding domain were conducted by use of clustal X 1.83 (Thompson et al., 1997). The previously identified conserved positive charged amino acids are indicated by stars (Abouhaidar and Lai, 1989). The arrows indicate the amino acids important for pCymMV-M2 to systemically infect N. benthamiana. The viruses, abbreviation and accession number used in alignment are described below. Cymbidium mosaic virus (CymMV, accession number AY571289); Potato aucuba mosaic virus (PAMV, accession number NC_003632; Narcissus mosaic virus (NMV, accession number NC_001441); Scallion virus X (ScaVX, accession number NC_003400); Papaya mosaic virus (PapMV, accession number NC_001748). (B). The concentration of recombinant CPs used in this experiment derived from clones pCymMV-M1 (M1-CP; Fig. 1), -M2 (M2-CP; Fig. 1) and -M2-CP-GL/AP (M2-CP-GL/AP; Fig. 6) and Glutathione-S-transferase (GST) derived from clones (pGEX 2T-1, Pharmacia Biosciences, Inc., New Jersey, USA) are shown. (C) Control experiments using M1 and M2 biotin-labeled RNA only (lane 1 and 2, respectively), or M1 and M2 RNA incubated with GST (lane 3 and 4, respectively) are shown. Because no RNA–protein binding occurred in these control experiments, RNA was detected only in S. (D) The results of experiments using RNA–protein combinations, M1 RNA/M1-CP (lane 1), M2 RNA/M1-CP (lane 2), M1 RNA/M2-CP (lane 3), M2 RNA/M2-CP (lane 4), M1 RNA/M2-CP-GL/AP (lane 5) and M2 RNA/M2-CP-GL/AP (lane 6), are shown. Different concentrations of sodium chloride (in milimolars; mM) added in incubation buffer are indicated. For convenience, the RNA–protein combinations used in the experiments are also indicated in the closed boxes. We repeated this experiment three times and one result is shown. The average S/P ratios were derived from the average of three independent experiments, and data were analyzed by Dunnett's T test. ⁎indicates significant difference (P < 0.01).