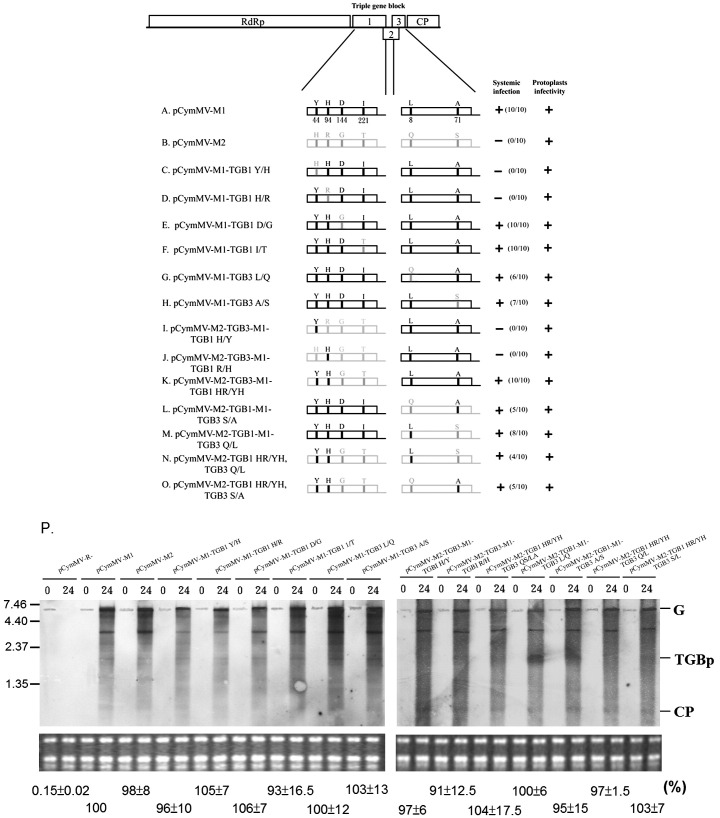
Fig. 8.
Schematic representation of TGBp1 mutants and infectivity assay between pCymMV-M1 and pCymMV-M2. (A–O) Rectangles represent ORFs encoded by CymMV genomic RNA, RNA-dependent RNA polymerase (RdRp), triple gene block ORFs 1, 2, and 3 and capsid protein (CP). Black and gray lines indicate different amino acids between pCymMV-M1 and pCymMV-M2, respectively. Positions of amino acids are indicated. Chimeric viruses competent in protoplast accumulation and systemic infection in N. benthamiana plants are indicated by +, and the ratio of systemic infected to total inoculated plants is indicated. Systemic infection was detected 2 weeks post-inoculation by RT-PCR. (P) Protoplast infectivity was detected 24 h post-inoculation by northern blot hybridization, and the ribosomal RNA used for a loading control are indicated. Genomic RNA (G), TGBp, and CP subgenomic RNA are indicated. The pCymMV-R- used as a negative control is illustrated in Fig. 1. The average percentage of relative real-time RT-PCR quantification (from 3 independent experiments) of CymMV RNA from CymMV clone-infected protoplasts at 24 h post-inoculation is indicated below the gels. The accumulation of pCymMV-M1 was set at 100% for relative quantification. Numbers at the left correspond to positions of marker RNAs (sizes in 1000 nucleotides) analyzed in the same gel.