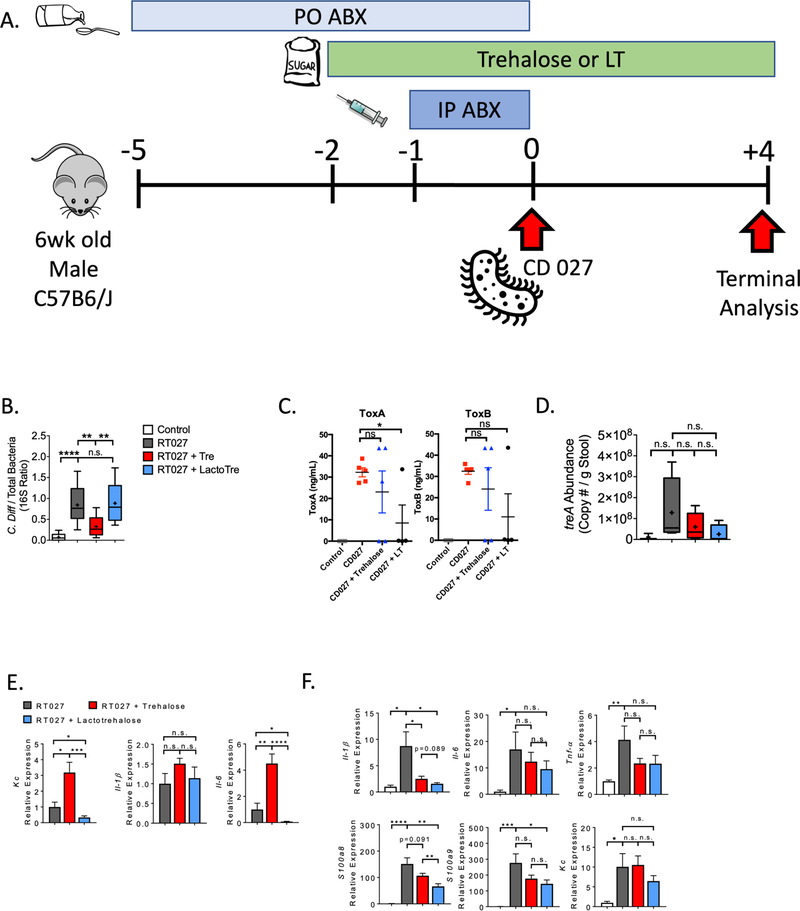
Figure 6. lactotrehalose reduces toxin and rectal inflammatory gene expression following CD027 infection in vivo.
A. Experimental design for CD027 infection and analysis. B. Quantification of CD027:total 16S ribosomal DNA ratio in stool from mice 96 h after CD027 infection following pre-treatment with or without trehalose or lactotrehalose (3% in water, ad libitum administered 2d prior to infection). C. ELISA-based C difficile Toxin A and B quantification in cecal contents from mice 72 h after CD027 infection following pre-treatment with or without trehalose or lactotrehalose (3% in water, ad libitum administered 2d prior to infection). D. and E. qRT-PCR quantification of treA and stool inflammatory marker gene expression in mice 96 h after CD027 infection following pre-treatment with or without trehalose or lactotrehalose. Marker gene expression was normalized against total 16S expression in each sample. F. Rectal tissue inflammatory marker gene mRNA expression by qRT-PCR analysis from mice infected with CD027 treated with or without trehalose or lactotrehalose. *, **, ***, ****, P < 0.05, 0.01, 0.001, or 0.0001 by two-tailed t-test with Bonferroni-Dunn post hoc correction for multiple comparisons.