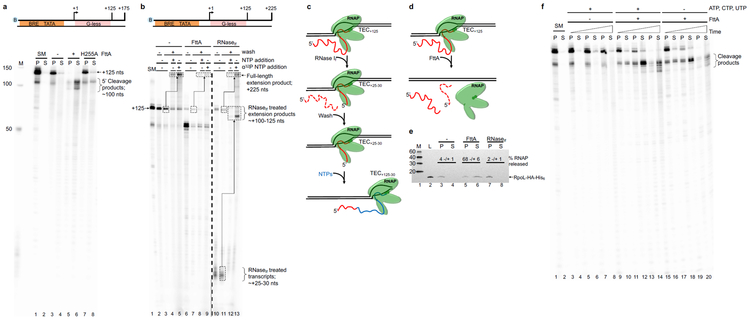
Figure 1. FttA is a bona fide archaeal transcription termination factor.
a. Transcripts within intact TECs are retained in pellet (P) fractions; transcripts released from terminated TECs partition into the supernatant (S). Radiolabeled transcripts within starting material (SM) TECs+125 and mock treated TECs+125 are retained in pellet fractions (lanes 1-4), whereas FttAWT addition results in cleavage of nascent transcripts and termination of most TECs (lanes 5-6). A catalytically deficient FttA variant (FttAH255A) abrogates cleavage and RNA release (lanes 7-8). Lane M contains 32P-labeled ssDNA markers. b. FttA-mediated termination is distinct from RNase treatment of intact TECs. TECs+125 (SM, lane 1) are resistant to repeated washes and readily resume elongation upon NTP addition to generate +225 nt transcripts (lanes 2-5). Dashed boxes and arrows denote +125 transcripts that are elongated to +225 nt transcripts; the specific activity of +225 transcripts can be increased by addition of additional 32P-α-UTP during resumed elongation. RNase If digestion of nascent transcripts associated with washed TECs+125 results in degradation of the nascent transcript to just ~20-30 nts, but TECs with shortened transcripts remain associated with the DNA and survive repeated washing (lanes 10-11). TECs~+25-30 resultant from RNase If treatment of TECs+125 readily resume elongation upon NTP addition to generate ~+125 nt full-length transcripts (lanes 12-13). Dashed boxes and arrows denote ~+25 transcripts that are elongated to ~+125 nt transcripts; the specific activity of ~+125 transcripts can be increased by addition of 32P-α-UTP during resumed elongation. FttA addition to TECs+125 disrupts most TECs with nascent transcript cleavage (lanes 6-9), results in release of most TECs from the template and cleaved transcripts cannot be extended by NTP addition (lanes 8-9). c and d. Diagrams of the fate of TECs+125 following RNase If and FttA treatment, respectively. e. FttA releases RNAP from the DNA template into solution confirming dissociation of the TEC and bona fide FttA-mediated transcription termination. RNAP is tracked and quantified by Western blots (n = 3 independent replicates) with anti-HA antibodies that recognize the modified RpoL-subunit. f. FttA is not reliant on NTP hydrolysis to inactivate TECs, cleave nascent transcripts and terminate transcription. For panels a, b f: Similar results were observed in 4 independent experiments.